教你使用Apache搭建Http下載服務器
目錄
- 前言
- Apache快速上手
- 修改端口號
- 設置訪問限制
- 配置文件參數詳解
- 限制連接量
- 封禁ip
- 設置賬號密碼訪問
- 參考
前言
前段時間因為某些原因,幾大主流網盤都無法使用,正好手頭上有臺閑置的云服務器,于是就想來搭建一個文件下載服務,用戶只需通過一個鏈接就能下載軟件。
Apache快速上手
經過調研,發現Ubuntu采用Apache2這個軟件就可以快速滿足我的需求。
安裝Apache2
apt-get install apache2
安裝好之后,啟動Apache2服務:
/etc/init.d/apache2 start
查看啟動狀態:
/etc/init.d/apache2 status
然后,訪問服務器的公網ip或域名,就可以看到如下界面,此時說明Apache正常工作:

最后在/var/www/html路徑下,刪除index.html,上傳自己想要被下載的文件,再次訪問,就可以進行下載了。
(注:如果是云服務器,還需要在安全組開放80和443端口號)
同時,也可以通過域名/文件名的方式直接給別人一個鏈接,進行下載。

如果有一臺單獨的服務器用于臨時文件的分享,這樣很快就搞定了。
下面來繼續進行深入研究,考慮更現實的場景。
修改端口號
Apache2默認采用的是80端口號,因此直接通過公網ip或域名就能訪問。現實中,很多服務器本身就部署了許多其它服務,80端口號往往被占用,因此就需要將Apache2改成其它訪問端口。
修改端口,首先需要修改/etc/apache2/ports.conf這個文件:
這里吧80改成其它不沖突的端口號,我這里以1024為例
#Listen 80Listen 1024<IfModule ssl_module>Listen 443</IfModule><IfModule mod_gnutls.c>Listen 443</IfModule>
然后修改/etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf
#<VirtualHost *:80><VirtualHost *:1024># The ServerName directive sets the request scheme, hostname and port that# the server uses to identify itself. This is used when creating
注:這個文件中還有一個DocumentRoot,修改該參數可以調整文件系統的根路徑。
修改完成之后,重啟apache2:
/etc/init.d/apache2 restart
此時,就可以通過訪問域名:1024的形式訪問到同樣內容,例如我的服務器訪問url為http://xdxsb.top:1024
設置訪問限制
個人服務器很容易遭到別人的攻擊,如果有人開好多線程來反復請求下載,這就將導致流量帶寬消耗巨大,甚至會讓服務器宕機。因此,長期提供下載服務的服務器必須設置訪問限制。
配置文件參數詳解
訪問限制主要涉及到/etc/apache2/apache2.conf這個配置文件,首先來對該文件進行解讀。
這個文件內容如下:
# This is the main Apache server configuration file. It contains the
# configuration directives that give the server its instructions.
# See http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/ for detailed information about
# the directives and /usr/share/doc/apache2/README.Debian about Debian specific
# hints.
#
#
# Summary of how the Apache 2 configuration works in Debian:
# The Apache 2 web server configuration in Debian is quite different to
# upstream's suggested way to configure the web server. This is because Debian's
# default Apache2 installation attempts to make adding and removing modules,
# virtual hosts, and extra configuration directives as flexible as possible, in
# order to make automating the changes and administering the server as easy as
# possible.
# It is split into several files forming the configuration hierarchy outlined
# below, all located in the /etc/apache2/ directory:
#
# /etc/apache2/
# |-- apache2.conf
# | `-- ports.conf
# |-- mods-enabled
# | |-- *.load
# | `-- *.conf
# |-- conf-enabled
# | `-- *.conf
# `-- sites-enabled
# `-- *.conf
#
#
# * apache2.conf is the main configuration file (this file). It puts the pieces
# together by including all remaining configuration files when starting up the
# web server.
#
# * ports.conf is always included from the main configuration file. It is
# supposed to determine listening ports for incoming connections which can be
# customized anytime.
#
# * Configuration files in the mods-enabled/, conf-enabled/ and sites-enabled/
# directories contain particular configuration snippets which manage modules,
# global configuration fragments, or virtual host configurations,
# respectively.
#
# They are activated by symlinking available configuration files from their
# respective *-available/ counterparts. These should be managed by using our
# helpers a2enmod/a2dismod, a2ensite/a2dissite and a2enconf/a2disconf. See
# their respective man pages for detailed information.
#
# * The binary is called apache2. Due to the use of environment variables, in
# the default configuration, apache2 needs to be started/stopped with
# /etc/init.d/apache2 or apache2ctl. Calling /usr/bin/apache2 directly will not
# work with the default configuration.
# Global configuration
#
#
# ServerRoot: The top of the directory tree under which the server's
# configuration, error, and log files are kept.
#
# NOTE! If you intend to place this on an NFS (or otherwise network)
# mounted filesystem then please read the Mutex documentation (available
# at <URL:http://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/core.html#mutex>);
# you will save yourself a lot of trouble.
#
# Do NOT add a slash at the end of the directory path.
#
#ServerRoot "/etc/apache2"
#
# The accept serialization lock file MUST BE STORED ON A LOCAL DISK.
#
#Mutex file:${APACHE_LOCK_DIR} default
#
# The directory where shm and other runtime files will be stored.
#
DefaultRuntimeDir ${APACHE_RUN_DIR}
#
# PidFile: The file in which the server should record its process
# identification number when it starts.
# This needs to be set in /etc/apache2/envvars
#
PidFile ${APACHE_PID_FILE}
#
# Timeout: The number of seconds before receives and sends time out.
#
Timeout 300
#
# KeepAlive: Whether or not to allow persistent connections (more than
# one request per connection). Set to "Off" to deactivate.
#
KeepAlive On
#
# MaxKeepAliveRequests: The maximum number of requests to allow
# during a persistent connection. Set to 0 to allow an unlimited amount.
# We recommend you leave this number high, for maximum performance.
#
MaxKeepAliveRequests 100
#
# KeepAliveTimeout: Number of seconds to wait for the next request from the
# same client on the same connection.
#
KeepAliveTimeout 5
# These need to be set in /etc/apache2/envvars
User ${APACHE_RUN_USER}
Group ${APACHE_RUN_GROUP}
#
# HostnameLookups: Log the names of clients or just their IP addresses
# e.g., www.apache.org (on) or 204.62.129.132 (off).
# The default is off because it'd be overall better for the net if people
# had to knowingly turn this feature on, since enabling it means that
# each client request will result in AT LEAST one lookup request to the
# nameserver.
#
HostnameLookups Off
# ErrorLog: The location of the error log file.
# If you do not specify an ErrorLog directive within a <VirtualHost>
# container, error messages relating to that virtual host will be
# logged here. If you *do* define an error logfile for a <VirtualHost>
# container, that host's errors will be logged there and not here.
#
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
#
# LogLevel: Control the severity of messages logged to the error_log.
# Available values: trace8, ..., trace1, debug, info, notice, warn,
# error, crit, alert, emerg.
# It is also possible to configure the log level for particular modules, e.g.
# "LogLevel info ssl:warn"
#
LogLevel warn
# Include module configuration:
IncludeOptional mods-enabled/*.load
IncludeOptional mods-enabled/*.conf
# Include list of ports to listen on
Include ports.conf
# Sets the default security model of the Apache2 HTTPD server. It does
# not allow access to the root filesystem outside of /usr/share and /var/www.
# The former is used by web applications packaged in Debian,
# the latter may be used for local directories served by the web server. If
# your system is serving content from a sub-directory in /srv you must allow
# access here, or in any related virtual host.
<Directory />
Options FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all denied
</Directory>
<Directory /usr/share>
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
<Directory /var/www/>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride None
Require all granted
</Directory>
#<Directory /srv/>
# Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
# AllowOverride None
# Require all granted
#</Directory>
# AccessFileName: The name of the file to look for in each directory
# for additional configuration directives. See also the AllowOverride
# directive.
#
AccessFileName .htaccess
#
# The following lines prevent .htaccess and .htpasswd files from being
# viewed by Web clients.
#
<FilesMatch "^\.ht">
Require all denied
</FilesMatch>
#
# The following directives define some format nicknames for use with
# a CustomLog directive.
#
# These deviate from the Common Log Format definitions in that they use %O
# (the actual bytes sent including headers) instead of %b (the size of the
# requested file), because the latter makes it impossible to detect partial
# requests.
#
# Note that the use of %{X-Forwarded-For}i instead of %h is not recommended.
# Use mod_remoteip instead.
#
LogFormat "%v:%p %h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %O \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" vhost_combined
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %O \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-Agent}i\"" combined
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %O" common
LogFormat "%{Referer}i -> %U" referer
LogFormat "%{User-agent}i" agent
# Include of directories ignores editors' and dpkg's backup files,
# see README.Debian for details.
# Include generic snippets of statements
IncludeOptional conf-enabled/*.conf
# Include the virtual host configurations:
IncludeOptional sites-enabled/*.conf
# vim: syntax=apache ts=4 sw=4 sts=4 sr noet
參數解釋:
PidFile:記錄服務器啟動進程號的文件
Timeout:接收和發送前超時秒數
KeepAlive:是否允許穩固的連接(每個連接有多個請求),設為"Off"則停用
MaxKeepAliveRequests:在穩固連接期間允許的最大請求數,設為0表示無限制接入
KeepAliveTimeout:在同一個連接上從同一臺客戶上接收請求的秒數
User/Group:運行的用戶和組
HostnameLookups:指定記錄用戶端的名字還是IP地址
例如,本指令為on時記錄主機名,如www.apache.org;為off時記錄IP地址,204.62.129.132。默認值為off,這要比設為on好得多,因為如果設為on則每個用戶端請求都將會至少造成對 nameserver 進行一次查詢。ErrorLog:錯誤日志文件定位
LogLevel:控制記錄在錯誤日志文件中的日志信息
可選值:debug,info,notice,warn,error,crit,alert,emergDirectory:在標簽對里面可以設置各文件夾屬性
Options:控制在特定目錄中將使用哪些服務器特性
- All:除MultiViews之外的所有特性,這是默認設置
- ExecCG:允許使用mod_cgi執行CGI腳本
- FollowSymLinks:服務器允許在此目錄中使用符號連接,如果此配置位于配置段中,則會被忽略
- Includes:允許使用mod_include提供的服務器端包含
- IncludesNOEXEC:允許服務器端包含,但禁用"#exec cmd"和"#exec cgi",但仍可以從ScriptAlias目錄使用"#include virtual"虛擬CGI腳本
- Indexes:如果一個映射到目錄的URL被請求,而此目錄中又沒有DirectoryIndex(例如:index.html),那么服務器會返回由mod_autoindex生成的一個格式化后的目錄列表
- MultiViews:允許使用mod_negotiation提供內容協商的"多重視圖"(MultiViews)
- SymLinksIfOwnerMatch:服務器僅在符號連接與其目的目錄或文件的擁有者具有相同的uid時才使用它。 如果此配置出現在配置段中,則將被忽略
AllowOverride:確定允許存在于.htaccess文件中的指令類型
語法:AllowOverride All|None|directive-type [directive-type]
如果此指令被設置為None ,那么.htaccess文件將被完全忽略。
directive-type可以是下列各組指令之一:- AuthConfig : 允許使用與認證授權相關的指令
- FileInfo : 允許使用控制文檔類型的指令、控制文檔元數據的指令、mod_rewrite中的指令、mod_actions中的Action指令
- Indexes : 允許使用控制目錄索引的指令
- Limit : 允許使用控制主機訪問的指令
Order:控制默認的訪問狀態與Allow和Deny指令生效的順序
- Deny,Allow : Deny指令在Allow指令之前被評估。默認允許所有訪問。任何不匹配Deny指令或者匹配Allow指令的客戶都被允許訪問
- Allow,Deny : Allow指令在Deny指令之前被評估。默認拒絕所有訪問。任何不匹配Allow指令或者匹配Deny指令的客戶都將被禁止訪問
- Mutual-failure : 只有出現在Allow列表并且不出現在Deny列表中的主機才被允許訪問。這種順序與"Order Allow,Deny"具有同樣效果
Allow:控制哪些主機可以訪問服務器的該區域。可以根據主機名、IP地址、 IP地址范圍或其他環境變量中捕獲的客戶端請求特性進行控制。
語法:Allow from all|host|env=env-variable [host|env=env-variable]Deny:控制哪些主機被禁止訪問服務器的該區域。可以根據主機名、IP地址、 IP地址范圍或其他環境變量中捕獲的客戶端請求特性進行控制。
語法:Deny from all|host|env=env-variable [host|env=env-variable]Require:訪問限制
- all granted:表示允許所有主機訪問
- all denied:表示拒絕所有主機訪問
- local:表示僅允許本地主機訪問
- [not] host <主機名或域名列表>:表示允許或拒絕指定主機或域名訪問
- [not] ip <IP地址或網段列表>:表示允許或拒絕指定的IP地址或網段訪問
AccessFileName:設置分布式配置文件的名字,默認為.htaccess
如果為某個目錄啟用了分布式配置文件功能,那么在向客戶端返回其中的文檔時,服務器將在這個文檔所在的各級目錄中查找此配置文件<FilesMatch"^.ht">:拒絕對.ht開頭文件的訪問,以保護.htaccess文件
LogFormat:定義訪問日志的格式
限制連接量
通過上面對配置文件參數的研究,注意到MaxKeepAliveRequests這個參數限制了對于單個連接最大的訪問量為100,因此無需擔心單線程腳本反復頻繁請求的問題。
那么對于高并發的請求,Apache是否有默認設置的策略呢?也是有的,從2.0開始,apache引入了MPM(Multi-Processing Module,多進程處理模塊),MPM有prefork, worker和event這三種模式[4],可以通過下面的命令查看當前apache所采用的模式:
apachectl -V | grep -i mpm
默認采用的應該是event模式。
這個模式的配置文件位于/etc/apache2/mods-availablempm_event.conf
默認參數:
<IfModule mpm_event_module>StartServers 2MinSpareThreads 25MaxSpareThreads 75ThreadLimit 64ThreadsPerChild 25MaxRequestWorkers150MaxConnectionsPerChild 0</IfModule>
參數解釋:
- StartServers:啟動時進程數
- MinSpareThreads:最小空閑線程數
- MaxSpareThreads:最大空閑線程數
- ThreadLimit:每個進程可以啟動的線程數量上限值
- ThreadsPerChild:每個進程可以啟動的線程數量
- MaxRequestWorkers:線程數量最大值
- MaxConnectionsPerChild:最大連接數限制
我這里沒去調整,先用JMeter來進行一個多線程并發測試:
JMeter下載地址:https://jmeter.apache.org/download_jmeter.cgi

解壓之后,運行apache-jmeter-5.5/bin/jmeter.bat,即可啟動。
創建一個線程組,我這設置了1000個線程數,時間設為0.01秒
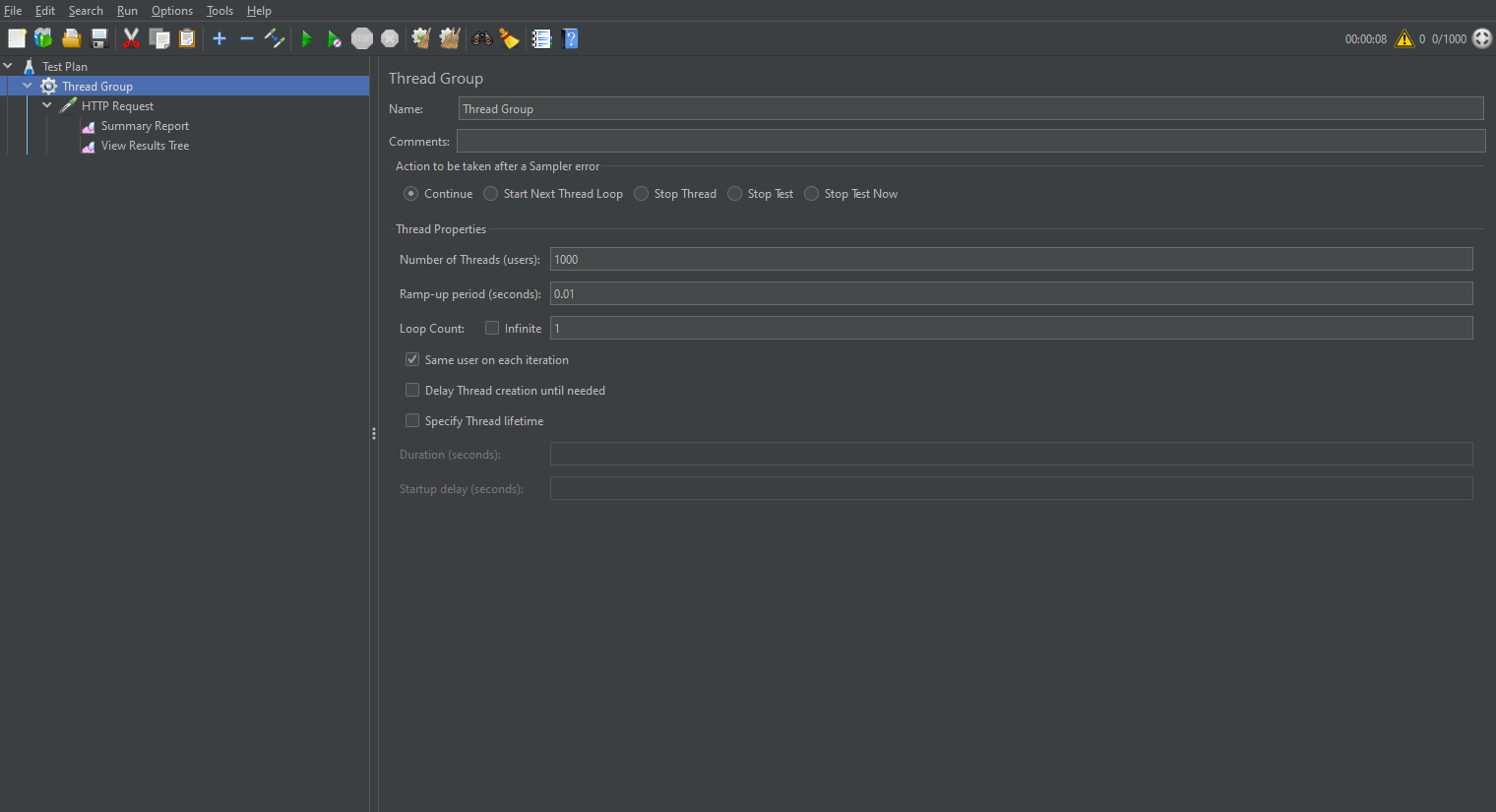
再設置HTTP請求,填寫請求域名,端口號,文件路徑
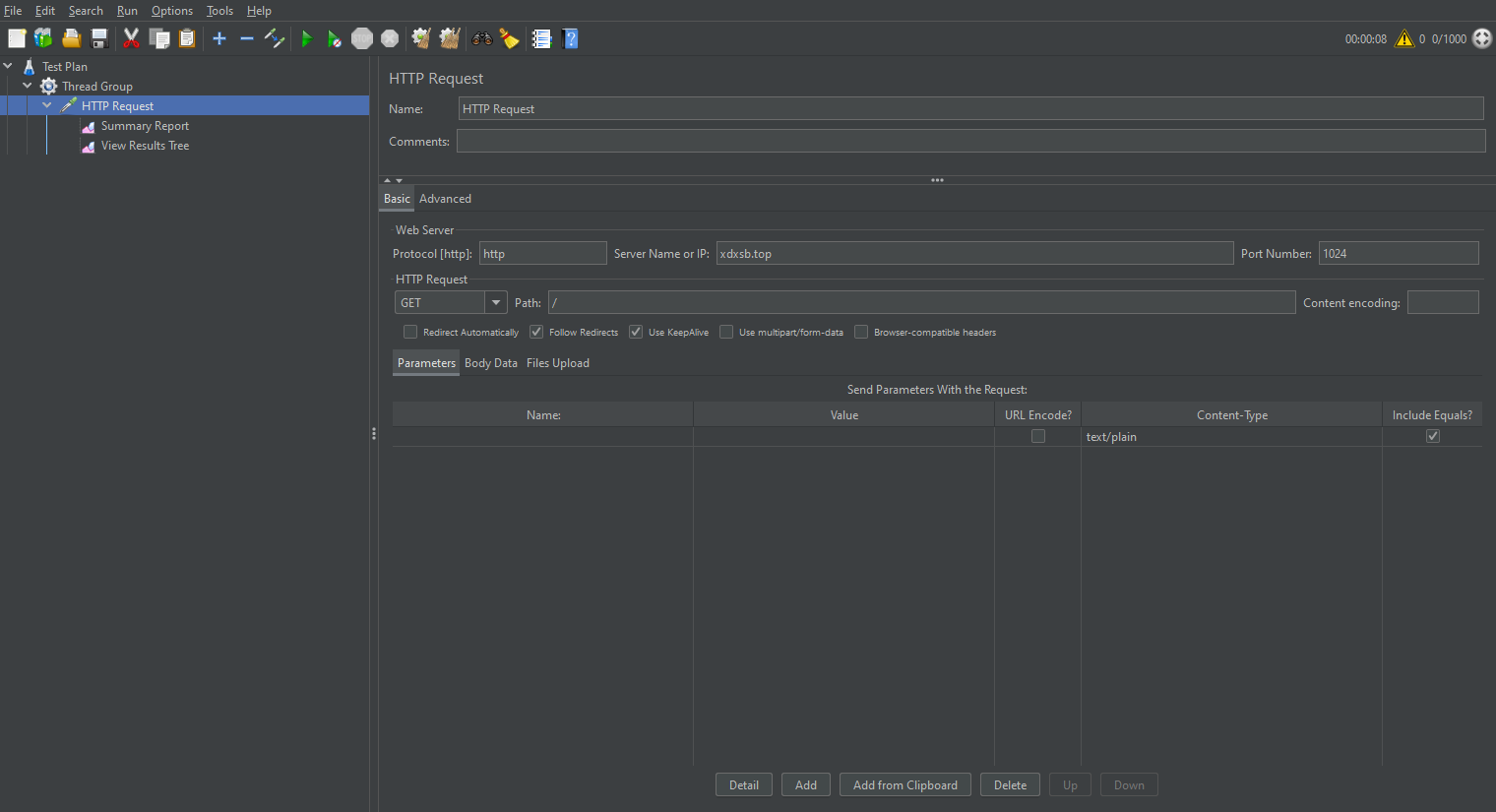
測試結果顯示,請求失敗率為16%,因此我這小破服務器,基本上1000個并發請求都難以滿足。

封禁ip
如果面對惡意攻擊,那最快解決問題的辦法無疑是封禁它的ip,這里嘗試一下封禁本機ip,看看是否有效。
首先查詢本機ip,直接在百度搜索ip,即可查詢到公網ip,注意這里一定要是公網ip,通過ipconfig查詢出的是內網ip。
修改配置文件:
vim /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
修改/var/www/文件內容:
<Directory /var/www/>Options Indexes FollowSymLinksAllowOverride None<RequireAll>Require all grantedRequire not ip 111.11.81.152</RequireAll></Directory>
重啟服務:
/etc/init.d/apache2 restart
再次訪問,發現權限受限,說明設置成功。
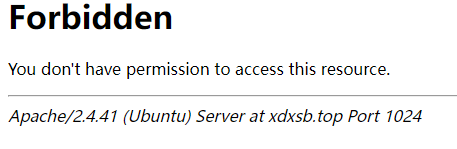
拓展:如果只允許某個固定ip訪問,那么可以這樣修改:
<Directory /var/www/>Options Indexes FollowSymLinksAllowOverride None# Require all grantedRequire ip 111.11.82.8</Directory>
設置賬號密碼訪問
對于某些私密文件,可以進一步配置賬號密碼進行身份驗證。
首先創建一個文件夾用來保存用戶信息:
mkdir -p /usr/local/conf
然后創建用戶:
htpasswd -c /usr/local/conf/.usr zstar
zstar是我創建的用戶名
輸入密碼后,Apache會以密文方式存儲密碼,可以通過下面的方式查看用戶名和密碼密文:
cat /usr/local/conf/.usr
再次修改配置文件:
vim /etc/apache2/apache2.conf
修改內容:
<Directory /var/www/>Options Indexes FollowSymLinksAllowOverride AllAuthName "apache"AuthType BasicAuthUserFile "/usr/local/conf/.usr"Require user zstar</Directory>
重啟服務:
/etc/init.d/apache2 restart
再次訪問,成功彈出登錄驗證,說明配置成功。

參考
[1]ubuntu搭建http服務器用于下載ubuntu文件:https://blog.csdn.net/yy1695990107/article/details/116976994
[2]Apache2 httpd.conf 配置詳解:https://blog.csdn.net/assassinice/article/details/78854139
[3]Apache的訪問控制:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_54434140/article/details/122249712
[4]apache2三種模式及參數調優:https://blog.csdn.net/zhihui1017/article/details/54959194
到此這篇關于教你使用Apache搭建Http下載服務器的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關Apache搭建Http下載服務器內容請搜索以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大家以后多多支持!
 網公網安備
網公網安備