Tomcat源碼解析之Web請求與處理
目錄
- 前言
- 一、EndPoint
- 二、ConnectionHandler
- 三、Coyote
- 四、容器責(zé)任鏈模式
前言
Tomcat最全UML類圖

Tomcat請求處理過程:
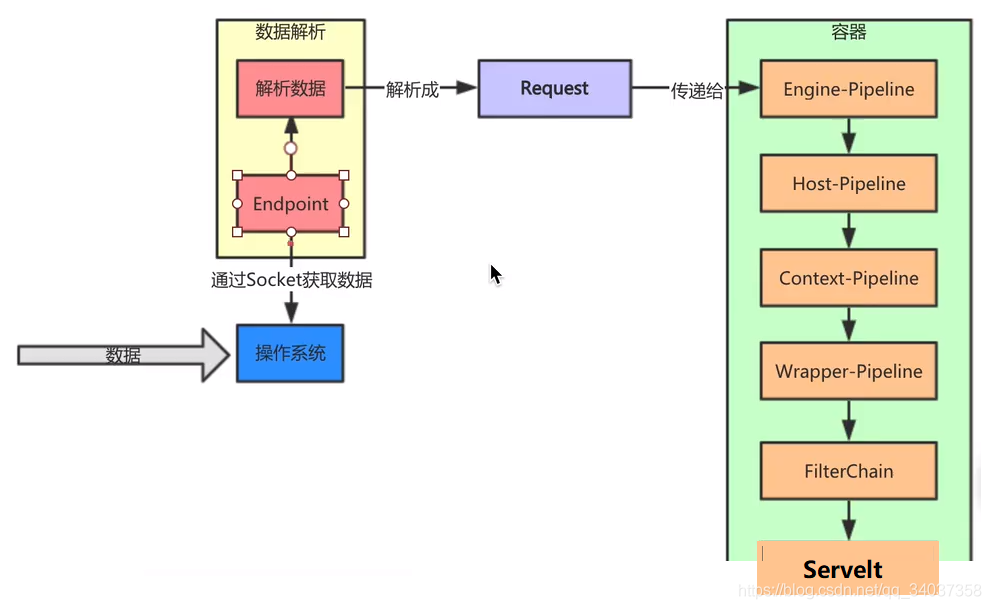
Connector對象創(chuàng)建的時候,會創(chuàng)建Http11NioProtocol的ProtocolHandler,在Connector的startInteral方法中,會啟動AbstractProtocol,AbstractProtocol啟動NioEndPoint進(jìn)行監(jiān)聽客戶端的請求,EndPoint接受到客戶端的請求之后,會交給Container去處理請求。請求從Engine開始經(jīng)過的所有容器都含有責(zé)任鏈模式,每經(jīng)過一個容器都會調(diào)用該容器的責(zé)任鏈對請求進(jìn)行處理。

一、EndPoint

默認(rèn)的EndPoint實現(xiàn)是NioEndPoint,NioEndPoint有四個內(nèi)部類,分別是Poller、Acceptor、PollerEvent、SocketProcessor、NioSocketWrapper。
(1)Acceptor負(fù)責(zé)監(jiān)聽用戶的請求,監(jiān)聽到用戶請求之后,調(diào)用getPoller0().register(channel);先將當(dāng)前請求封裝成PollerEvent,new PollerEvent(socket, ka, OP_REGISTER); 將當(dāng)前請求,封裝成注冊事件,并添加到PollerEvent隊列中,然后將PollerEvent注冊到Poller的Selector對象上面。
(2)Poller線程會一直遍歷可以處理的事件(netty的selestor),當(dāng)找到需要處理的事件之后,調(diào)用processKey(sk, socketWrapper);對,執(zhí)行要處理的PollerEvent的run方法,對請求進(jìn)行處理。
(3)PollerEvent繼承自Runnable接口,在其run方法里面,如果是PollerEvent的事件是注冊O(shè)P_REGISTER,那么就將當(dāng)前的socket注冊到Poller的selector上。
public void run() { if (interestOps == OP_REGISTER) {try { // 核心代碼,終于找到了!!!!! // 當(dāng)事件是注冊的時候,將當(dāng)前的NioSocketChannel注冊到Poller的Selector上。 socket.getIOChannel().register( socket.getPoller().getSelector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ, socketWrapper);} catch (Exception x) { log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.registerFail"), x);} } else {final SelectionKey key = socket.getIOChannel().keyFor(socket.getPoller().getSelector());try { if (key == null) {// The key was cancelled (e.g. due to socket closure)// and removed from the selector while it was being// processed. Count down the connections at this point// since it won"t have been counted down when the socket// closed.// SelectionKey被取消的時候需要將SelectionKey對應(yīng)的EndPoint的Connection計數(shù)器,減一socket.socketWrapper.getEndpoint().countDownConnection();((NioSocketWrapper) socket.socketWrapper).closed = true; } else {final NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = (NioSocketWrapper) key.attachment();if (socketWrapper != null) { //we are registering the key to start with, reset the fairness counter. int ops = key.interestOps() | interestOps; socketWrapper.interestOps(ops); key.interestOps(ops);} else { socket.getPoller().cancelledKey(key);} }} catch (CancelledKeyException ckx) { try {socket.getPoller().cancelledKey(key); } catch (Exception ignore) { }} }}(4)Poller線程內(nèi)會執(zhí)行keyCount = selector.select(selectorTimeout);獲取當(dāng)前需要處理的SelectionKey的數(shù)量,然后當(dāng)keyCount大于0時,會獲取selector的迭代器,遍歷所有需要的selectionkey,并對其進(jìn)行處理。在這里將socket的事件封裝成NioSocketWrapper。
// 得到selectedKeys的迭代器Iterator<SelectionKey> iterator = keyCount > 0 ? selector.selectedKeys().iterator() : null; // 遍歷所有的SelectionKey,并對其進(jìn)行處理 while (iterator != null && iterator.hasNext()) { SelectionKey sk = iterator.next(); iterator.remove(); NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = (NioSocketWrapper) sk.attachment(); // Attachment may be null if another thread has called // cancelledKey() // 如果有attachment,就處理 if (socketWrapper != null) { // 處理事件 processKey(sk, socketWrapper); } }processKey在處理SelectionKey,如果當(dāng)前Poller已經(jīng)關(guān)閉,就取消key。SelectionKey對應(yīng)的Channel如果發(fā)生讀事件,就調(diào)用AbatractEndPoint.processSocket執(zhí)行讀操作processSocket(attachment, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ, true),如果SelectionKey對應(yīng)的Channel發(fā)生寫事件,就執(zhí)行processSocket(attachment, SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE, true);讀大于寫。socket的事件處理調(diào)用的是AbatractEndPoint的processSocket方法。
protected void processKey(SelectionKey sk, NioSocketWrapper attachment) { try { if (close) { // 如果Poller已經(jīng)關(guān)閉了,就取消key cancelledKey(sk); } else if (sk.isValid() && attachment != null) { if (sk.isReadable() || sk.isWritable()) { if (attachment.getSendfileData() != null) { processSendfile(sk, attachment, false); } else { unreg(sk, attachment, sk.readyOps()); boolean closeSocket = false; // Read goes before write // 讀優(yōu)于寫 // 如果SelectionKey對應(yīng)的Channel已經(jīng)準(zhǔn)備好了讀 // 就對NioSocketWrapper進(jìn)行讀操作 if (sk.isReadable()) { if (!processSocket(attachment, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ, true)) { closeSocket = true; } } // 如果SelectionKey對應(yīng)的Channel已經(jīng)準(zhǔn)備好了寫 // 就對NioSocketWrapper進(jìn)行寫操作 if (!closeSocket && sk.isWritable()) { if (!processSocket(attachment, SocketEvent.OPEN_WRITE, true)) { closeSocket = true; } } if (closeSocket) { // 如果已經(jīng)關(guān)閉了,就取消key cancelledKey(sk); } } } }AbatractEndPoint.processSocket方法首先從緩存中獲取SocketProcessor類,如果緩存中沒有就創(chuàng)建一個,SocketProcessorBase接口對應(yīng)的就是NioEndPoint.SocketProcessor,也就是Worker。將對應(yīng)的SocketProcessor類放入到線程池中執(zhí)行。
public boolean processSocket(SocketWrapperBase<S> socketWrapper, SocketEvent event, boolean dispatch) { // 得到socket的處理器 // Connector在構(gòu)造函數(shù)里面已經(jīng)指定了協(xié)議:org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol。 SocketProcessorBase<S> sc = processorCache.pop(); if (sc == null) { // 如果沒有,就創(chuàng)建一個Socket的處理器。創(chuàng)建的時候指定socketWrapper以及socket的事件。 sc = createSocketProcessor(socketWrapper, event); } else { sc.reset(socketWrapper, event); } //socket的處理交給了線程池去處理。 Executor executor = getExecutor(); if (dispatch && executor != null) { executor.execute(sc); } else { sc.run(); }(5)NioEndPoint.NioSocketWrapper,是Socket的封裝類,增強(qiáng)類,將Socket與其他對象建立關(guān)聯(lián)。
public static class NioSocketWrapper extends SocketWrapperBase<NioChannel> { private final NioSelectorPool pool;private Poller poller = null; // 輪詢的Poller private int interestOps = 0;private CountDownLatch readLatch = null;private CountDownLatch writeLatch = null;private volatile SendfileData sendfileData = null;private volatile long lastRead = System.currentTimeMillis();private volatile long lastWrite = lastRead;private volatile boolean closed = false;(6)NioEndPoint.SocketProcessor(Worker)繼承了Runnable接口,負(fù)責(zé)對socket的g各種事件進(jìn)行處理。讀事件、寫事件、停止時間、超時事件、斷連事件、錯誤時間、連接失敗事件。

SocketProcessor的doRun方法,會根據(jù)SocketState進(jìn)行處理,SocketState 為STOP、DISCONNECT或者ERROR的時候就進(jìn)行關(guān)閉,SocketWrapperBase對應(yīng)的selector事件,得到指定的Handler處理器進(jìn)行處理。
@Override protected void doRun() { NioChannel socket = socketWrapper.getSocket(); SelectionKey key = socket.getIOChannel().keyFor(socket.getPoller().getSelector()); try { int handshake = -1; try { if (key != null) { if (socket.isHandshakeComplete()) { // 是否已經(jīng)握手成功,不需要TLS(加密)握手,就讓處理器對socket和event的組合進(jìn)行處理。 handshake = 0; } else if (event == SocketEvent.STOP || event == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT || event == SocketEvent.ERROR) { // 不能夠完成TLS握手,就把他認(rèn)為是TLS握手失敗。 handshake = -1; } else { handshake = socket.handshake(key.isReadable(), key.isWritable()); // The handshake process reads/writes from/to the // socket. status may therefore be OPEN_WRITE once // the handshake completes. However, the handshake // happens when the socket is opened so the status // must always be OPEN_READ after it completes. It // is OK to always set this as it is only used if // the handshake completes. // 握手從/向socket讀/寫時,握手一旦完成狀態(tài)應(yīng)該為OPEN_WRITE, // 握手是在套接字打開時發(fā)生的,因此在完成后狀態(tài)必須始終為OPEN_READ // 始終設(shè)置此選項是可以的,因為它僅在握手完成時使用。 event = SocketEvent.OPEN_READ; } } } catch (IOException x) { handshake = -1; if (log.isDebugEnabled()) log.debug("Error during SSL handshake", x); } catch (CancelledKeyException ckx) { handshake = -1; } if (handshake == 0) { SocketState state = SocketState.OPEN; // Process the request from this socket if (event == null) { // 調(diào)用處理器進(jìn)行處理。 // NioEndPoint的默認(rèn)Handler是Http11的 // 這里的Handler是AbstractProtocol.ConnectionHandler // 這個Handler的設(shè)置方法是: // 首先在Connector類的構(gòu)造函數(shù)中,將默認(rèn)的ProtocolHandler設(shè)置為org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol // AbstractHttp11Protocol的構(gòu)造函數(shù)里面創(chuàng)建了Handler類ConnectionHandler state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ); } else { state = getHandler().process(socketWrapper, event); } // 如果返回的狀態(tài)是SocketState,那么就關(guān)掉連接 if (state == SocketState.CLOSED) { close(socket, key); } } else if (handshake == -1) { getHandler().process(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.CONNECT_FAIL); close(socket, key); } else if (handshake == SelectionKey.OP_READ) { // 如果是SelectionKey.OP_READ,也就是讀事件的話,就將OP_READ時間設(shè)置到socketWrapper socketWrapper.registerReadInterest(); } else if (handshake == SelectionKey.OP_WRITE) { // 如果是SelectionKey.OP_WRITE,也就是讀事件的話,就將OP_WRITE事件設(shè)置到socketWrapper socketWrapper.registerWriteInterest(); }二、ConnectionHandler

(1)ConnectionHandler用于根據(jù)Socket連接找到相應(yīng)的Engine處理器。
上面是SocketProcessor的doRun方法,執(zhí)行了getHandler().process(socketWrapper, SocketEvent.OPEN_READ);;process方法是首先在Map緩存中查找當(dāng)前socket是否存在對應(yīng)的processor,如果不存在,再去可循環(huán)的處理器棧中查找是否存在,如果不存在就創(chuàng)建相應(yīng)的Processor,然后將新創(chuàng)建的Processor與Socket建立映射,存在connection的Map中。在任何一個階段得到Processor對象之后,會執(zhí)行processor的process方法state = processor.process(wrapper, status);
protected static class ConnectionHandler<S> implements AbstractEndpoint.Handler<S> {private final AbstractProtocol<S> proto;private final RequestGroupInfo global = new RequestGroupInfo();private final AtomicLong registerCount = new AtomicLong(0);// 終于找到了這個集合,給Socket和處理器建立連接// 對每個有效鏈接都會緩存進(jìn)這里,用于連接選擇一個合適的Processor實現(xiàn)以進(jìn)行請求處理。private final Map<S, Processor> connections = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();// 可循環(huán)的處理器棧private final RecycledProcessors recycledProcessors = new RecycledProcessors(this); @Overridepublic SocketState process(SocketWrapperBase<S> wrapper, SocketEvent status) { if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.process",wrapper.getSocket(), status)); } if (wrapper == null) {// wrapper == null 表示Socket已經(jīng)被關(guān)閉了,所以不需要做任何操作。return SocketState.CLOSED; } // 得到wrapper內(nèi)的Socket對象 S socket = wrapper.getSocket(); // 從Map緩沖區(qū)中得到socket對應(yīng)的處理器。 Processor processor = connections.get(socket); if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.connectionsGet",processor, socket)); } // Timeouts are calculated on a dedicated thread and then // dispatched. Because of delays in the dispatch process, the // timeout may no longer be required. Check here and avoid // unnecessary processing. // 超時是在專用線程上計算的,然后被調(diào)度。 // 因為調(diào)度過程中的延遲,可能不再需要超時。檢查這里,避免不必要的處理。 if (SocketEvent.TIMEOUT == status && (processor == null || !processor.isAsync() && !processor.isUpgrade() || processor.isAsync() && !processor.checkAsyncTimeoutGeneration())) {// This is effectively a NO-OPreturn SocketState.OPEN; } // 如果Map緩存存在該socket相關(guān)的處理器 if (processor != null) {// Make sure an async timeout doesn"t fire// 確保沒有觸發(fā)異步超時getProtocol().removeWaitingProcessor(processor); } else if (status == SocketEvent.DISCONNECT || status == SocketEvent.ERROR) {// Nothing to do. Endpoint requested a close and there is no// longer a processor associated with this socket.// SocketEvent事件是關(guān)閉,或者SocketEvent時間出錯,此時不需要做任何操作。// Endpoint需要一個CLOSED的信號,并且這里不再有與這個socket有關(guān)聯(lián)了return SocketState.CLOSED; } ContainerThreadMarker.set(); try {// Map緩存不存在該socket相關(guān)的處理器if (processor == null) { String negotiatedProtocol = wrapper.getNegotiatedProtocol(); // OpenSSL typically returns null whereas JSSE typically // returns "" when no protocol is negotiated // OpenSSL通常返回null,而JSSE通常在沒有協(xié)議協(xié)商時返回"" if (negotiatedProtocol != null && negotiatedProtocol.length() > 0) {// 獲取協(xié)商協(xié)議UpgradeProtocol upgradeProtocol = getProtocol().getNegotiatedProtocol(negotiatedProtocol);if (upgradeProtocol != null) { // 升級協(xié)議為空 processor = upgradeProtocol.getProcessor(wrapper, getProtocol().getAdapter()); if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.processorCreate", processor)); }} else if (negotiatedProtocol.equals("http/1.1")) { // Explicitly negotiated the default protocol. // Obtain a processor below.} else { // TODO: // OpenSSL 1.0.2"s ALPN callback doesn"t support // failing the handshake with an error if no // protocol can be negotiated. Therefore, we need to // fail the connection here. Once this is fixed, // replace the code below with the commented out // block. if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.negotiatedProcessor.fail",negotiatedProtocol)); } return SocketState.CLOSED; /* * To replace the code above once OpenSSL 1.1.0 is * used. // Failed to create processor. This is a bug. throw new IllegalStateException(sm.getString( "abstractConnectionHandler.negotiatedProcessor.fail", negotiatedProtocol)); */} }}// 經(jīng)過上面的操作,processor還是null的話。if (processor == null) { // 從recycledProcessors可循環(huán)processors中獲取processor processor = recycledProcessors.pop(); if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.processorPop", processor)); }}if (processor == null) { // 創(chuàng)建處理器 processor = getProtocol().createProcessor(); register(processor); if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.processorCreate", processor)); }}processor.setSslSupport(wrapper.getSslSupport(getProtocol().getClientCertProvider()));// 將socket和processor建立關(guān)聯(lián)。connections.put(socket, processor);SocketState state = SocketState.CLOSED;do { // 調(diào)用processor的process方法。 state = processor.process(wrapper, status); // processor的process方法返回升級狀態(tài) if (state == SocketState.UPGRADING) {// Get the HTTP upgrade handler// 得到HTTP的升級句柄UpgradeToken upgradeToken = processor.getUpgradeToken();// Retrieve leftover input// 檢索剩余輸入ByteBuffer leftOverInput = processor.getLeftoverInput();if (upgradeToken == null) { // Assume direct HTTP/2 connection UpgradeProtocol upgradeProtocol = getProtocol().getUpgradeProtocol("h2c"); if (upgradeProtocol != null) {// Release the Http11 processor to be re-usedrelease(processor);// Create the upgrade processorprocessor = upgradeProtocol.getProcessor(wrapper, getProtocol().getAdapter());wrapper.unRead(leftOverInput);// Associate with the processor with the connectionconnections.put(socket, processor); } else {if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) { getLog().debug(sm.getString( "abstractConnectionHandler.negotiatedProcessor.fail", "h2c"));}// Exit loop and trigger appropriate clean-upstate = SocketState.CLOSED; }} else { HttpUpgradeHandler httpUpgradeHandler = upgradeToken.getHttpUpgradeHandler(); // Release the Http11 processor to be re-used release(processor); // Create the upgrade processor processor = getProtocol().createUpgradeProcessor(wrapper, upgradeToken); if (getLog().isDebugEnabled()) {getLog().debug(sm.getString("abstractConnectionHandler.upgradeCreate",processor, wrapper)); } wrapper.unRead(leftOverInput); // Associate with the processor with the connection connections.put(socket, processor); // Initialise the upgrade handler (which may trigger // some IO using the new protocol which is why the lines // above are necessary) // This cast should be safe. If it fails the error // handling for the surrounding try/catch will deal with // it. if (upgradeToken.getInstanceManager() == null) {httpUpgradeHandler.init((WebConnection) processor); } else {ClassLoader oldCL = upgradeToken.getContextBind().bind(false, null);try { httpUpgradeHandler.init((WebConnection) processor);} finally { upgradeToken.getContextBind().unbind(false, oldCL);} }} }} while (state == SocketState.UPGRADING); (2)以Http11協(xié)議為例,執(zhí)行的是Http11Processor,Http11Processor的祖父類AbstractProcessorLight實現(xiàn)了process方法,process調(diào)用了service模板方法,service模板方法是由Http11Processor進(jìn)行實現(xiàn)的。service方法最重要的操作是執(zhí)行getAdapter().service(request, response);
@Override public SocketState service(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper) throws IOException { // 上面省略n行 // 調(diào)用Coyote的service方法 getAdapter().service(request, response); // 下面省略n行三、Coyote
回顧一下CoyoteAdapter的創(chuàng)建是在Connector的initInternal方法。
@Override public SocketState service(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper) throws IOException { // 上面省略n行 // 調(diào)用Coyote的service方法 getAdapter().service(request, response); // 下面省略n行Coyote的作用就是coyote.Request和coyote.Rsponse轉(zhuǎn)成HttpServletRequest和HttpServletRsponse。然后,因為Connector在init的時候,將自己注入到了CoyoteAdapter中,所以,直接通過connector.getService()方法就可以拿到Service,然后從Service開始調(diào)用責(zé)任鏈模式,進(jìn)行處理。
@Override public SocketState service(SocketWrapperBase<?> socketWrapper) throws IOException { // 上面省略n行 // 調(diào)用Coyote的service方法 getAdapter().service(request, response); // 下面省略n行四、容器責(zé)任鏈模式
接下來就是從StandradEngine開始的責(zé)任鏈模式。首先執(zhí)行StandradEngine的責(zé)任鏈模式,找到合適的Engine,合適的Engine在通過責(zé)任鏈模式找到合適的Context,直到找到StandardWrapperValve。最后執(zhí)行到StandardWrapperValve的invoke方法。首先查看Context和Wrapper是不是不可用了,如果可用,并且Servelt還沒有被初始化,就執(zhí)行初始化操作。如果是單線程模式就直接返回之前創(chuàng)建好的Servelt,如果是多線程模式,就先創(chuàng)建一個Servelt對象進(jìn)行返回。
@Override public final void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {// 初始化我們需要的本地變量boolean unavailable = false;Throwable throwable = null;// This should be a Request attribute...long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();// 原子類AtomicInteger,CAS操作,表示請求的數(shù)量。requestCount.incrementAndGet();StandardWrapper wrapper = (StandardWrapper) getContainer();Servlet servlet = null;Context context = (Context) wrapper.getParent();// 檢查當(dāng)前的Context應(yīng)用是否已經(jīng)被標(biāo)注為不可以使用if (!context.getState().isAvailable()) { // 如果當(dāng)前應(yīng)用不可以使用的話,就報503錯誤。 response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE, sm.getString("standardContext.isUnavailable")); unavailable = true;}// 檢查Servelt是否被標(biāo)記為不可使用if (!unavailable && wrapper.isUnavailable()) { container.getLogger().info(sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable", wrapper.getName())); long available = wrapper.getAvailable(); if ((available > 0L) && (available < Long.MAX_VALUE)) {response.setDateHeader("Retry-After", available);response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE,sm.getString("standardWrapper.isUnavailable",wrapper.getName())); } else if (available == Long.MAX_VALUE) {response.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_FOUND,sm.getString("standardWrapper.notFound",wrapper.getName())); } unavailable = true;}// Servelt是第一次調(diào)用的時候初始化try { if (!unavailable) {// 如果此時Servelt還沒有被初始化,就分配一個Servelt實例來處理request請求。servlet = wrapper.allocate(); }/// 省略代碼..........................................// // 給該request創(chuàng)建Filter過濾鏈。Filter過濾鏈執(zhí)行完之后,會執(zhí)行ServeltApplicationFilterChain filterChain =ApplicationFilterFactory.createFilterChain(request, wrapper, servlet);// Call the filter chain for this request// NOTE: This also calls the servlet"s service() methodtry { if ((servlet != null) && (filterChain != null)) {// Swallow output if neededif (context.getSwallowOutput()) { try {SystemLogHandler.startCapture();if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) { request.getAsyncContextInternal().doInternalDispatch();} else { // 調(diào)用過濾鏈 filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse());}/// 省略代碼..........................................到此這篇關(guān)于Tomcat源碼解析之Web請求與處理的文章就介紹到這了,更多相關(guān)Tomcat的Web請求與處理內(nèi)容請搜索以前的文章或繼續(xù)瀏覽下面的相關(guān)文章希望大家以后多多支持!
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備