mysql學習筆記之完整的select語句用法實例詳解
本文實例講述了mysql學習筆記之完整的select語句用法。分享給大家供大家參考,具體如下:
本文內容: 完整語法 去重選項 字段別名 數據源 where group by having order by limit首發日期:2018-04-11
完整語法:先給一下完整的語法,后面將逐一來講解。
基礎語法:select 字段列表 from 數據源;
完整語法:select 去重選項 字段列表 [as 字段別名] from 數據源 [where子句] [group by 子句] [having子句] [order by 子句] [limit子句];
去重選項:: 去重選項就是是否對結果中完全相同的記錄(所有字段數據都相同)進行去重: all:不去重 distinct:去重 語法:select 去重選項 字段列表 from 表名;示例:
去重前: ,去重后
,去重后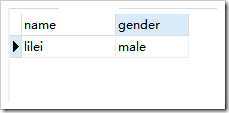
create table student(name varchar(15),gender varchar(15));insert into student(name,gender) values('lilei','male');insert into student(name,gender) values('lilei','male');select * from student;select distinct * from student;補充: 注意:去重針對的是查詢出來的記錄,而不是存儲在表中的記錄。如果說僅僅查詢的是某些字段,那么去重針對的是這些字段。字段別名: 字段別名是給查詢結果中的字段另起一個名字 字段別名只會在當次查詢結果中生效。 字段別名一般都是輔助了解字段意義(比如我們定義的名字是name,我們希望返回給用戶的結果顯示成姓名)、簡寫字段名 語法:select 字段 as 字段別名 from 表名;
示例:
使用前: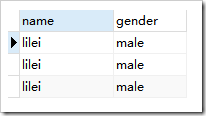 ,使用后
,使用后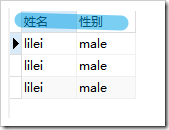
create table student(name varchar(15),gender varchar(15));insert into student(name,gender) values('lilei','male');insert into student(name,gender) values('lilei','male');select * from student;select name as '姓名',gender as '性別' from student;數據源: 事實上,查詢的來源可以不是“表名”,只需是一個二維表即可。那么數據來源可以是一個select結果。 數據源可以是單表數據源,多表數據源,以及查詢語句單表:select 字段列表 from 表名; 多表: select 字段列表 from 表名1,表名2,…; 【多表查詢時是將每個表中的x條記錄與另一個表y條記錄組成結果,組成的結果的記錄條數為x*y】【可以稱為笛卡爾積】 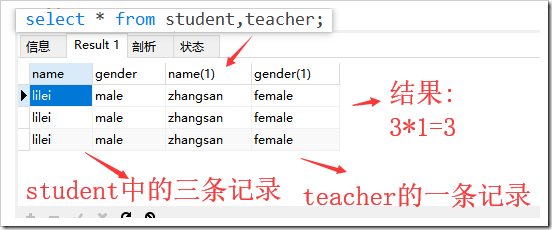 查詢語句:select 字段列表 fromr (select語句) as 表別名;【這是將一個查詢結果作為一個查詢的目標二維表,需要將查詢結果定義成一個表別名才能作為數據源】
查詢語句:select 字段列表 fromr (select語句) as 表別名;【這是將一個查詢結果作為一個查詢的目標二維表,需要將查詢結果定義成一個表別名才能作為數據源】
-- 示例select name from (select * from student) as d; where子句: where子句是用于篩選符合條件的結果的。
where幾種語法:
基于值: = : where 字段 =值 ;查找出對應字段等于對應值的記錄。(相似的,<是小于對應值,<=是小于等于對應值,>是大于對應值,>=是大于等于對應值,!=是不等于),例如:where name = ’lilei’ like:where 字段 like 值 ;功能與 = 相似 ,但可以使用模糊匹配來查找結果。例如:where name like ’li%’ 基于值的范圍: in: where 字段 in 范圍;查找出對應字段的值在所指定范圍的記錄。例如:where age in (18,19,20) not in : where 字段 not in 范圍;查找出對應字段的值不在所指定范圍的記錄。例如:where age not in (18,19,20) between x and y :where 字段 between x and y;查找出對應字段的值在閉區間[x,y]范圍的記錄。例如:where age between 18 and 20。 條件復合: or : where 條件1 or 條件2… ; 查找出符合條件1或符合條件2的記錄。 and: where 條件1 and 條件2… ; 查找出符合條件1并且符合條件2的記錄。 not : where not 條件1 ;查找出不符合條件的所有記錄。 &&的功能與and相同;||與or功能類似,!與not 功能類似。 補充: where是從磁盤中獲取數據的時候就進行篩選的。所以某些在內存是才有的東西where無法使用。(字段別名什么的是本來不是“磁盤中的數據”(是在內存這中運行時才定義的),所以where無法使用,一般都依靠having來篩選).select name as n ,gender from student where name ='lilei';-- select name as n ,gender from student where n ='lilei'; --報錯select name as n ,gender from student having n ='lilei';group by 子句: group by 可以將查詢結果依據字段來將結果分組。 語法:select 字段列表 from 表名 group by 字段; 【字段可以有多個,實際就是二次分組】
-- 示例select name,gender,count(name) as '組員' from student as d group by name;select name,gender,count(name) as '組員' from student as d group by name,gender;補充: 實際上,group by 的作用主要是統計(使用情景很多,比如說統計某人的總分數,學生中女性的數量。。),所以一般會配合一些統計函數來使用: count(x):統計每組的記錄數,x是*時代表記錄數,為字段名時代表統計字段數據數(除去NULL) max(x):統計最大值,x是字段名 min(x):統計最小值,x是字段名 avg(x):統計平均值,x是字段名 sum(x):統計總和,x是字段名 group by 字段 后面還可以跟上asc或desc,代表分組后是否根據字段排序。having子句: having功能與where類似,不過having的條件判斷發生在數據在內存中時,所以可以使用在內存中才發生的數據,如“分組”,“字段別名”等。 語法:select 字段列表 from 表名 having 條件;【操作符之類的可以參考where的,增加的只是一些“內存”中的篩選條件】
-- 示例select name as n ,gender from student having n ='lilei';select name,gender,count(*) as '組員' from student as d group by name,gender having count(*) >2 ;-- 這里只顯示記錄數>2的分組order by 子句: order by 可以使查詢結果按照某個字段來排序 語法:select 字段列表 from 表名 order by 字段 [asc|desc]; 字段可以有多個,從左到右,后面的排序基于前面的,(比如:先按name排序,再按gender排序,后面的gender排序是針對前面name排序時name相同的數據) asc代表排序是遞增的 desc代表是遞減的 也可以指定某個字段的排序方法,比如第一個字段遞增,第二個遞減。只需要在每個字段后面加asc或desc即可(雖然默認不加是遞增,但還是加上更清晰明確)。
-- 示例select * from student order by name;select * from student order by name,gender;select * from student order by name asc,gender desc;limit子句: limit是用來限制結果數量的。與wherehaving等配合使用時,可以限制匹配出的結果。但凡是涉及數量的時候都可以使用limit(這里只是強調limit的作用,不要過度理解) 語法:select 字段列表 from 表名 limit [offset,] count; count是數量 offset是起始位置,offset從0開始,可以說是每條記錄的索引號
-- 示例select * from student limit 1;select * from student limit 3,1;select * from student where name ='lilei' limit 1;select * from student where name ='lilei' limit 3,1;
更多關于MySQL相關內容感興趣的讀者可查看本站專題:《MySQL查詢技巧大全》、《MySQL事務操作技巧匯總》、《MySQL存儲過程技巧大全》、《MySQL數據庫鎖相關技巧匯總》及《MySQL常用函數大匯總》
希望本文所述對大家MySQL數據庫計有所幫助。
相關文章:
 網公網安備
網公網安備