詳解Jackson的基本用法
Jackson 是當(dāng)前用的比較廣泛的,用來序列化和反序列化 json 的 Java 的開源框架。Jackson 社 區(qū)相對比較活躍,更新速度也比較快, 從 Github 中的統(tǒng)計來看,Jackson 是最流行的 json 解析器之一 。 Spring MVC 的默認(rèn) json 解析器便是 Jackson。Jackson 優(yōu)點很多。Jackson 所依賴的 jar 包較少 ,簡單易用。與其他 Java 的 json 的框架 Gson 等相比, Jackson 解析大的 json 文件速度比較快;Jackson 運行時占用內(nèi)存比較低,性能比較好;Jackson 有靈活的 API,可以很容易進行擴展和定制。
Jackson 的 1.x 版本的包名是 org.codehaus.jackson ,當(dāng)升級到 2.x 版本時,包名變?yōu)?com.fasterxml.jackson,本文討論的內(nèi)容是基于最新的 Jackson 的 2.9.1 版本。
二、Jackson的核心模塊 jackson-core,核心包,提供基于'流模式'解析的相關(guān) API,它包括 JsonPaser 和 JsonGenerator。 Jackson 內(nèi)部實現(xiàn)正是通過高性能的流模式 API 的 JsonGenerator 和 JsonParser 來生成和解析 json。 jackson-annotations,注解包,提供標(biāo)準(zhǔn)注解功能; jackson-databind ,數(shù)據(jù)綁定包, 提供基于'對象綁定' 解析的相關(guān) API ( ObjectMapper ) 和'樹模型' 解析的相關(guān) API (JsonNode);基于'對象綁定' 解析的 API 和'樹模型'解析的 API 依賴基于'流模式'解析的 API。清單 1.在 pom.xml 的 Jackson 的配置信息
<dependency> <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> <version>2.9.1</version> </dependency>
jackson-databind 依賴 jackson-core 和 jackson-annotations,當(dāng)添加 jackson-databind 之后, jackson-core 和 jackson-annotations 也隨之添加到 Java 項目工程中。在添加相關(guān)依賴包之后,就可以使用 Jackson。
三、ObjectMapper的使用Jackson 最常用的 API 就是基于'對象綁定' 的 ObjectMapper。下面是一個 ObjectMapper 的使用的簡單示例。
清單 2 . ObjectMapper 使用示例
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); Person person = new Person(); person.setName('Tom'); person.setAge(40); String jsonString = mapper.writerWithDefaultPrettyPrinter() .writeValueAsString(person); Person deserializedPerson = mapper.readValue(jsonString, Person.class);
ObjectMapper 通過 writeValue 系列方法 將 java 對 象序列化 為 json,并 將 json 存 儲成不同的格式,String(writeValueAsString),Byte Array(writeValueAsString),Writer, File,OutStream 和 DataOutput。
ObjectMapper 通過 readValue 系列方法從不同的數(shù)據(jù)源像 String , Byte Array, Reader,F(xiàn)ile,URL, InputStream 將 json 反序列化為 java 對象。
四、信息配置在調(diào)用 writeValue 或調(diào)用 readValue 方法之前,往往需要設(shè)置 ObjectMapper 的相關(guān)配置信息。這些配置信息應(yīng)用 java 對象的所有屬性上。示例如下:
清單 3 . 配置信息使用示例
//在反序列化時忽略在 json 中存在但 Java 對象不存在的屬性 mapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false); //在序列化時日期格式默認(rèn)為 yyyy-MM-dd’T’HH:mm:ss.SSSZ mapper.configure(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS,false) //在序列化時忽略值為 null 的屬性 mapper.setSerializationInclusion(Include.NON_NULL); //忽略值為默認(rèn)值的屬性 mapper.setDefaultPropertyInclusion(Include.NON_DEFAULT);
更多配置信息可以查看 Jackson 的 DeserializationFeature,SerializationFeature 和 I nclude。
五、Jackson注解的使用Jackson 根據(jù)它的默認(rèn)方式序列化和反序列化 java 對象,若根據(jù)實際需要,靈活的調(diào)整它的默認(rèn)方式,可以使用 Jackson 的注解。常用的注解及用法如下。
表 1. Jackson 的 常用注解
注解 用法 @JsonProperty 用于屬性,把屬性的名稱序列化時轉(zhuǎn)換為另外一個名稱。示例: @JsonProperty('birth_ d ate') private Date birthDate; @JsonFormat 用于屬性或者方法,把屬性的格式序列化時轉(zhuǎn)換成指定的格式。示例: @JsonFormat(timezone = 'GMT+8', pattern = 'yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm') public Date getBirthDate() @JsonPropertyOrder 用于類, 指定屬性在序列化時 json 中的順序 , 示例: @JsonPropertyOrder({ 'birth_Date', 'name' }) public class Person @JsonCreator 用于構(gòu)造方法,和 @JsonProperty 配合使用,適用有參數(shù)的構(gòu)造方法。 示例: @JsonCreator public Person(@JsonProperty('name')String name) {…} @JsonAnySetter 用于屬性或者方法,設(shè)置未反序列化的屬性名和值作為鍵值存儲到 map 中 @JsonAnySetter public void set(String key, Object value) { map.put(key, value); } @JsonAnyGetter 用于方法 ,獲取所有未序列化的屬性 public Map<String, Object> any() { return map; } 六、Jackson示例6.1、Jackson ObjectMapper ExampleObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();String carJson = '{ 'brand' : 'Mercedes', 'doors' : 5 }';try { Car car = objectMapper.readValue(carJson, Car.class); System.out.println('car brand = ' + car.getBrand()); System.out.println('car doors = ' + car.getDoors());} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();}public class Car { private String brand = null; private int doors = 0; public String getBrand() { return this.brand; } public void setBrand(String brand){ this.brand = brand;} public int getDoors() { return this.doors; } public void setDoors (int doors) { this.doors = doors; }}6.2、從Reader讀取對象
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();String carJson ='{ 'brand' : 'Mercedes', 'doors' : 4 }';Reader reader = new StringReader(carJson);Car car = objectMapper.readValue(reader, Car.class);6.3、從File中讀取對象
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();File file = new File('data/car.json');Car car = objectMapper.readValue(file, Car.class);6.4、從URL中讀取對象
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();URL url = new URL('file:data/car.json');Car car = objectMapper.readValue(url, Car.class);6.5、從InputStream讀取對象
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();InputStream input = new FileInputStream('data/car.json');Car car = objectMapper.readValue(input, Car.class);6.6、從字節(jié)數(shù)組中讀取對象
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();String carJson ='{ 'brand' : 'Mercedes', 'doors' : 5 }';byte[] bytes = carJson.getBytes('UTF-8');Car car = objectMapper.readValue(bytes, Car.class);6.7、從JSON數(shù)組字符中讀取對象數(shù)組
String jsonArray = '[{'brand':'ford'}, {'brand':'Fiat'}]';ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();Car[] cars2 = objectMapper.readValue(jsonArray, Car[].class);6.8、從JSON數(shù)組字符中讀取對象列表
String jsonArray =“[{”brand “:”ford “},{”brand “:”Fiat “}]”;ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();List <Car> cars1 = objectMapper.readValue(jsonArray,new TypeReference <List <Car >>(){});6.9、從JSON字符串中讀取映射為map
String jsonObject =“{”brand “:”ford “,”doors “:5}”;ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();Map <String,Object> jsonMap = objectMapper.readValue(jsonObject, new TypeReference <Map <String,Object >>(){});6.10、樹模型
String carJson ='{ 'brand' : 'Mercedes', 'doors' : 5 }';ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();try { JsonNode jsonNode = objectMapper.readValue(carJson, JsonNode.class);} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();}
JSON字符串被解析為JsonNode對象而不是Car對象,只需將JsonNode.class第二個參數(shù)傳遞給readValue()方法而不是Car.class本教程前面的示例中使用的方法。
該ObjectMapper班也有一個特殊的readTree(),它總是返回一個方法JsonNode。以下是JsonNode使用該ObjectMapperreadTree()方法將JSON解析為a的示例:
String carJson ='{ 'brand' : 'Mercedes', 'doors' : 5 }';ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();try { JsonNode jsonNode = objectMapper.readTree(carJson);} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();}
JsonNode類
String carJson ='{ 'brand' : 'Mercedes', 'doors' : 5,' +' 'owners' : ['John', 'Jack', 'Jill'],' +' 'nestedObject' : { 'field' : 'value' } }';ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();try { JsonNode jsonNode = objectMapper.readValue(carJson, JsonNode.class); JsonNode brandNode = jsonNode.get('brand'); String brand = brandNode.asText(); System.out.println('brand = ' + brand); JsonNode doorsNode = jsonNode.get('doors'); int doors = doorsNode.asInt(); System.out.println('doors = ' + doors); JsonNode array = jsonNode.get('owners'); JsonNode jsonNode = array.get(0); String john = jsonNode.asText(); System.out.println('john = ' + john); JsonNode child = jsonNode.get('nestedObject'); JsonNode childField = child.get('field'); String field = childField.asText(); System.out.println('field = ' + field);} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();}6.11、將Object轉(zhuǎn)換為JsonNode
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();Car car = new Car();car.brand = 'Cadillac';car.doors = 4;JsonNode carJsonNode = objectMapper.valueToTree(car);6.12、將JsonNode轉(zhuǎn)換為Object
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();String carJson = '{ 'brand' : 'Mercedes', 'doors' : 5 }';JsonNode carJsonNode = objectMapper.readTree(carJson);Car car = objectMapper.treeToValue(carJsonNode);6.13、使用Jackson ObjectMapper讀取和編寫YAML6.13.1、示例1
只是yaml字符串和對象的互轉(zhuǎn),不涉及yaml文件的處理
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;import com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.yaml.YAMLFactory;import java.io.IOException;public class YamlJacksonExample { public static void main(String[] args) {ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(new YAMLFactory());Employee employee = new Employee('John Doe', '[email protected]');String yamlString = null;try { yamlString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(employee);} catch (JsonProcessingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); // normally, rethrow exception here - or don’t catch it at all.} }}
該yamlString變量包含Employee在執(zhí)行此代碼后序列化為YAML數(shù)據(jù)格式的對象。
以下是Employee再次將YAML文本讀入對象的示例:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;import com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.yaml.YAMLFactory;import java.io.IOException;public class YamlJacksonExample { public static void main(String[] args) {ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(new YAMLFactory());Employee employee = new Employee('John Doe', '[email protected]');String yamlString = null;try { yamlString = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(employee);} catch (JsonProcessingException e) { e.printStackTrace(); // normally, rethrow exception here - or don’t catch it at all.}try { Employee employee2 = objectMapper.readValue(yamlString, Employee.class); System.out.println('Done');} catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace();} }}6.13.2、示例2
yaml文件的讀取和寫入
定義Employee實體類
package com.example.jackjson;import lombok.Data;@Datapublic class Employee { public Employee() { } public Employee(String name, String email) {this.name = name;this.email = email; } String name; String email;}
創(chuàng)建要讀取的yml EmployeeYaml.yml文件,并初始化一條數(shù)據(jù)
name: test
email: [email protected]
創(chuàng)建要寫入的yml文件,EmployeeYamlOutput.yml (空文件)
測試類
package com.example.jackjson;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.SerializationFeature;import com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.yaml.YAMLFactory;import com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat.yaml.YAMLGenerator;import java.io.File;import java.io.IOException;public class YamlJacksonExample { public static void main(String[] args) {try { //從yaml文件讀取數(shù)據(jù) reaedYamlToEmployee(); //寫入yaml文件 reaedEmployeeToYaml();} catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace();} } /** * 從yaml文件讀取數(shù)據(jù) * @throws IOException */ private static void reaedYamlToEmployee() throws IOException {ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(new YAMLFactory());Employee employee = mapper.readValue(new File('src/test/java/com/example/jackjson/EmployeeYaml.yml'), Employee.class);System.out.println(employee.getName() + '********' + employee.getEmail()); } /** * 寫入yaml文件 * @throws IOException */ private static void reaedEmployeeToYaml() throws IOException {//去掉三個破折號ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(new YAMLFactory().disable(YAMLGenerator.Feature.WRITE_DOC_START_MARKER));//禁用掉把時間寫為時間戳mapper.disable(SerializationFeature.WRITE_DATES_AS_TIMESTAMPS);Employee employee = new Employee('test2', '[email protected]');mapper.writeValue(new File('src/test/java/com/example/jackjson/EmployeeYamlOutput.yml'), employee); }}
讀取文件的打印輸出
test********[email protected]
Process finished with exit code 0
寫入文件的輸出
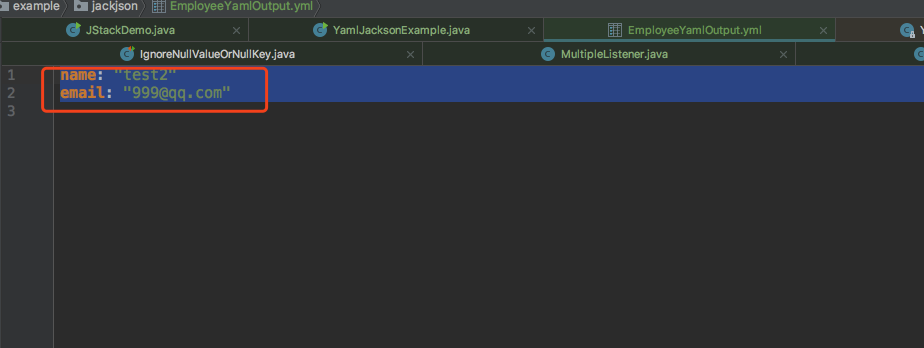
以上就是詳解Jackson的基本用法的詳細(xì)內(nèi)容,更多關(guān)于Java Jackson的資料請關(guān)注好吧啦網(wǎng)其它相關(guān)文章!
相關(guān)文章:

 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備