Spring RestTemplate基本使用介紹
上篇文件介紹Eureka服務的文章中,我們介紹到consumer從Eureka中通過LoadBalancerClient獲取到服務端地址信息后通過RestTemplate來遠程調用服務的場景,本文來具體介紹下RestTemplate的使用
RestTemplate
SpringRestTemplate是Spring 提供的用于訪問 Rest 服務的客端, RestTemplate提供了多種便捷訪問遠程Http服務的方法,能夠大大提高客戶端的編寫效率,所以很多客戶端比如Android或者第三方服務商都是使用RestTemplate 請求 restful服務
1.環境搭建
為了演示RestTemplate的使用,我們創建兩個SpringBoot項目,一個provider作為server端,一個consumer作為服務調用方法
2.API方法介紹
API 說明 getForEntity() 發送一個HTTP GET請求,返回的ResponseEntity包含了響應體所映射成的對象 getForObject() 發送一個HTTP GET請求,返回的請求體將映射為一個對象 postForEntity() POST 數據到一個URL,返回包含一個對象的ResponseEntity,這個對象是從響應體中映射得到的 postForObject() POST 數據到一個URL,返回根據響應體匹配形成的對象 headForHeaders() 發送HTTP HEAD請求,返回包含特定資源URL的HTTP頭 optionsForAllow() 發送HTTP OPTIONS請求,返回對特定URL的Allow頭信息 postForLocation() POST 數據到一個URL,返回新創建資源的URL put() PUT 資源到特定的URL delete() 在特定的URL上對資源執行HTTP DELETE操作 exchange() 在URL上執行特定的HTTP方法,返回包含對象的ResponseEntity,這個對象是從響應體中映射得到的 execute() 在URL上執行特定的HTTP方法,返回一個從響應體映射得到的對象
3.具體使用
我們通過常用的http協議的四種請求方式來看下效果
3.1 無參請求
我們先來看下服務端請求方法不需要接收參數,
getForEntity
通過getForEntity來實現
服務端
/** * 無參,返回字符串 * @return */ @GetMapping('/server1') public String server1String(){ System.out.println('服務端被訪問了...'); return 'success'; }
調用
/** * RestTemplate 訪問 provider的第一個服務 server1 */@Testpublic void contextLoads() { String url = 'http://localhost:8080/server1'; RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); ResponseEntity<String> entity = restTemplate.getForEntity(url, String.class); // 獲取響應的狀態 HttpStatus statusCode = entity.getStatusCode(); // 獲取響應的header信息 HttpHeaders headers = entity.getHeaders(); // 獲取響應的body信息 String msg = entity.getBody(); System.out.println(statusCode); System.out.println(headers); System.out.println(msg);}
輸出結果
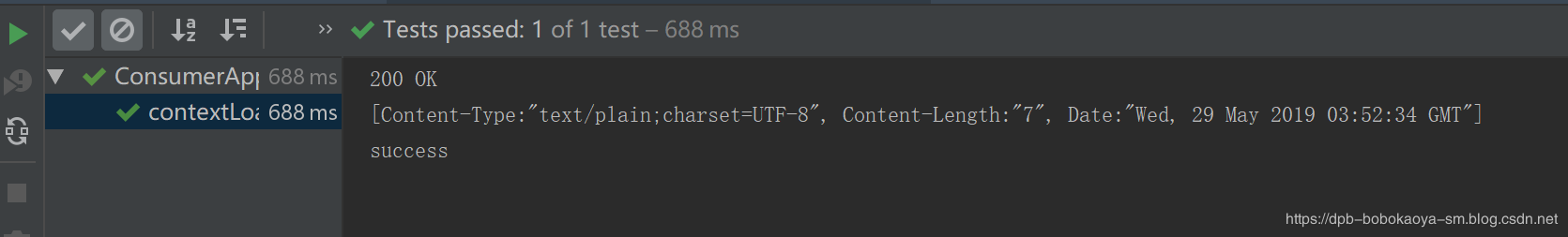
說明:
1.getForEntity()方法執行返回的類型是ResponseEntity<T>,ResponseEntity<T>是Spring對HTTP請求響應的封裝,包括了幾個重要的元素,如響應碼、contentType、contentLength、響應消息體等,在輸出結果中我們能夠看到2.getForEntity()的參數中第一個是請求地址,第二個是T對應的類型
getForObject
getForObject函數實際上是對getForEntity函數的進一步封裝,如果你只關注返回的消息體的內容,對其他信息都不關注,此時可以使用getForObject
/** * getForObject 訪問 */@Testpublic void contextLoadsObject() { String url = 'http://localhost:8080/server1'; RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); // 直接返回的就是我們需要的結果,但是獲取不到對應的響應狀態等信息 String msg = restTemplate.getForObject(url,String.class); System.out.println(msg);}
3.2 有參請求
服務端方法需要接收調用者傳遞的參數
/** * 有參,基本數據類型 返回字符串 * @return */ @RequestMapping('/server2') public String server2String(Integer id,String userName){ System.out.println('服務端被訪問了...'+id+' '+userName); return 'success--參數得到了'; } /** * 有參,基本數據類型 返回字符串 * @return */ @RequestMapping('/server3') public String server3String(User user){ System.out.println('服務端被訪問了...'+user); return 'success--參數得到了'; }
getForEntity
調用者可以通過兩種方式調用第一種方式通過數字占位符,最后是一個可變長度的參數,來一一替換前面的占位符
/*** 請求服務并且傳遞參數* 基本數據類型*/@Testpublic void testServer2(){// 參數在鏈接地址后 String url = 'http://localhost:8080/server2?id={1}&userName={2}'; RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); ResponseEntity<String> entity = restTemplate.getForEntity(url, String.class,5,'bobo'); System.out.println(entity.getBody());}
第二種就是使用name={name}這種形式,最后一個參數是一個map,map的key即為前邊占位符的名字,map的value為參數值
/** * 請求服務并且傳遞參數 * 基本數據類型 */@Testpublic void testServer3(){ String url = 'http://localhost:8080/server2?id={id}&userName={userName}'; Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put('id',6); map.put('userName','波波烤鴨'); RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); ResponseEntity<String> entity = restTemplate.getForEntity(url, String.class,map); System.out.println(entity.getBody());}
postForEntity
如果是post方式提交請求傳遞參數我們可以這樣使用,如下
服務端:注意要加@RequestBody注解
/** * 有參,基本數據類型 返回字符串 * @return */@RequestMapping('/server3')public String server3String(@RequestBody User user){ System.out.println('服務端被訪問了...'+user); return 'success--參數得到了';}
客戶端
/** * postForEntity(url,user,String.class) * url:請求地址 * user:請求提交的數據 * String.class 接收返回數據的類型 */@Testpublic void contextLoadsObject1() { String url = 'http://localhost:8080/server3'; RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); User user = new User(1,'bobo','中國'); // 直接返回的就是我們需要的結果,但是獲取不到對應的響應狀態等信息 String msg = restTemplate.postForEntity(url,user,String.class).getBody(); System.out.println(msg);}
3.3 返回自己類型
服務端返回的我們自定義類型的數據
/** * 返回自定義對象 * @return */ @RequestMapping('/server4') public User server4Object(){ System.out.println('服務端被訪問了...'); return new User(2,'李四','深圳'); }
客戶端:
/** * 返回類型為自定義類型 */@Testpublic void testServer5(){ String url = 'http://localhost:8080/server4'; RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate(); ResponseEntity<User> entity = restTemplate.getForEntity(url, User.class); System.out.println(entity.getBody());}
使用getForEntity和getForObject及postForEntity和postForObject都差不多,注意接收的類型即可。
3.4 返回的list帶泛型的場景
此處我們需要使用到exchange方法,特定如下
允許調用者指定HTTP請求的方法(GET,POST,PUT等) 可以在請求中增加body以及頭信息,其內容通過參‘HttpEntity<?>requestEntity’描述 exchange支持‘含參數的類型’(即泛型類)作為返回類型,該特性通過‘ParameterizedTypeReferenceresponseType’描述客戶端調用
/** * 返回 集合帶泛型 * @return */@RequestMapping('/server5')public List<User> server5List(){ System.out.println('服務端被訪問了...'); return Arrays.asList(new User(2,'李四1','深圳') ,new User(3,'李四2','深圳') ,new User(4,'李四3','深圳'));}

好了~RestTemplate的基本使用我們就介紹到此處,更多相關Spring RestTemplate使用內容請搜索好吧啦網以前的文章或繼續瀏覽下面的相關文章希望大家以后多多支持好吧啦網!
相關文章:
 網公網安備
網公網安備