Java注解使用及原理解析
基本特性
1、jdk 1.5之后才引入的。
2、用來(lái)說(shuō)明程序的。(注釋是給程序員看的,注解就是給電腦看的)
java注解的作用分類
1、編寫文檔:通過(guò)代碼標(biāo)識(shí)的注解生成文檔。【生成doc文檔】
2、代碼分析:通過(guò)代碼標(biāo)識(shí)的注解對(duì)代碼進(jìn)行分析。【使用反射】
3、編譯檢查:通過(guò)代碼標(biāo)識(shí)的注解讓編譯器能夠?qū)崿F(xiàn)基本的編譯檢查。【override】
測(cè)試類:
/** * 我的javadoc測(cè)試 */public class TestCode { /** * 計(jì)算兩個(gè)數(shù)的和 * @param a 整數(shù)a * @param b 整數(shù)b * @return 返回兩個(gè)數(shù)的和 */ public int add(int a, int b){ return a+b; }}
對(duì)于2、3兩點(diǎn)我們應(yīng)該是知道的。盡管可能不知道里面的原理。但是是平時(shí)都在用的。但是對(duì)于1點(diǎn)還可以生成doc文檔?
測(cè)試操作如下:
D:softjdkbinjavadoc.exe .TestCode.java -encoding utf-8 -docEncoding utf-8 -charset utf-8
生成了一大堆的東西:
打開TestCode.html可以發(fā)現(xiàn),我們的java api手冊(cè)就是這樣生產(chǎn)的。
注解來(lái)源分類
1、jdk自帶的注解,如常見的override(重寫校驗(yàn)),deprecated(表示棄用)
2、自定義的注解
1)格式, 以override為例:
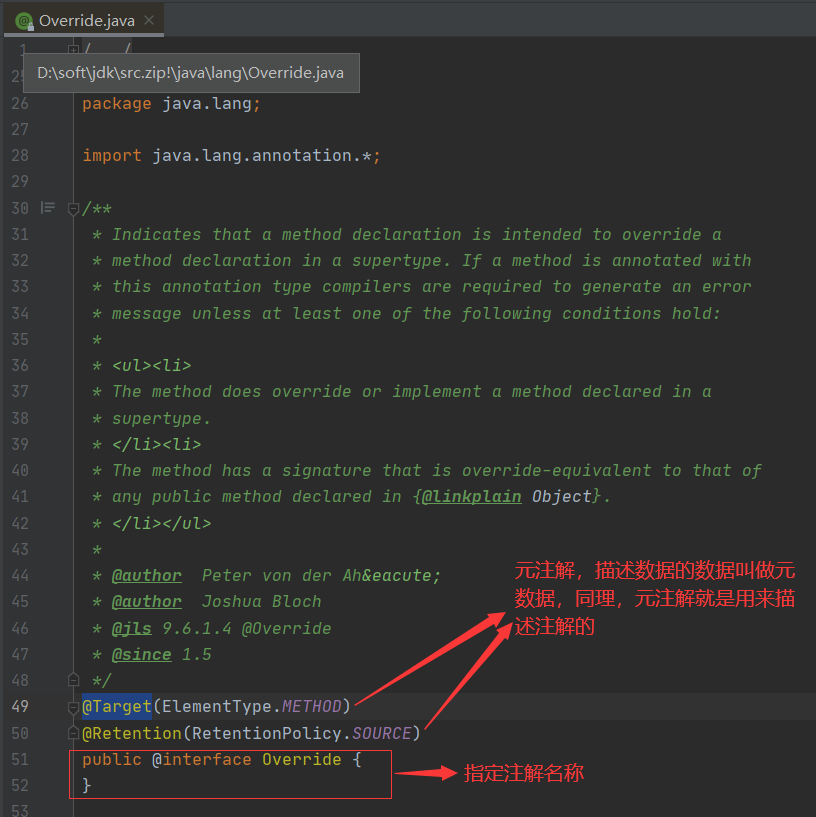
2)注解的本質(zhì)
我們編寫一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單的注解
MyAnnotation.java
public @interface MyAnnotation {}
我們通過(guò)編譯和反編譯看下最終是什么樣的結(jié)果:
D:softjdkbinjavac.exe MyAnnotation.java
D:softjdkbinjavap.exe MyAnnotation.class
結(jié)果如下:
public interface MyAnnotation extends java.lang.annotation.Annotation {
}
可以發(fā)現(xiàn)注解的本質(zhì)就是接口,這個(gè)接口繼承了jdk里面的Annotation接口。
3)注解的屬性
由于注解本質(zhì)為接口,那么里面可以定義未實(shí)現(xiàn)的方法。這些稱為注解的“屬性”。
屬性的返回類型有(返回值不能為void):
基本數(shù)據(jù)類型 String 枚舉 注解 以及以上四種類型的數(shù)組例子:
public enum Person { PS;}public @interface Annotation2 {}public @interface MyAnnotation { String stringValue(); int integerValue(); Person personValue(); Annotation2 myAnnotationValue(); String[] stringArrayValue();}
屬性的使用,需要注意幾點(diǎn):
定義了屬性在使用的時(shí)候就要給屬性賦值,除非設(shè)置default值。如:String stringValue() default 'aaa'; 如果屬性為value且屬性只有這一個(gè),那么value可以省略,直接填寫屬性值。 如果是數(shù)組,需要用{}包含起來(lái)。public @interface MyAnnotation { String stringValue() default 'xxx'; int integerValue(); String[] stringArrayValue();}public @interface Annotation2 { String value();}@MyAnnotation(integerValue = 1, stringArrayValue = {'aaa', 'bbb'})@Annotation2('default')public class TestCode { /** * 計(jì)算兩個(gè)數(shù)的和 * @param a 整數(shù)a * @param b 整數(shù)b * @return 返回兩個(gè)數(shù)的和 */ public int add(int a, int b){ return a+b; } @Override public String toString() { return super.toString(); }}
元注解
元注解是你在編寫注解的時(shí)候,上面加的注解,就是注解的注解。主要有4個(gè)。
@target, 用于指定注解的使用位置。如@Target(ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE),@Target(value = {ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.METHOD})。 @Inherited,表示父類加了這個(gè)注解,子類也自動(dòng)加上。 @Documented, 表示這個(gè)注解的信息在執(zhí)行javadoc的時(shí)候是否抽取到api文檔中。 @Retention,表示注解被保留的階段,java類,class文件,以及被jvm讀取。總共三種。RetentionPolicy.SOURCE, RetentionPolicy.CLASS, RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME元注解的內(nèi)容,可以到j(luò)dk源碼里面看一下,更有利于理解。
解析注解
這個(gè)是最關(guān)鍵了,以上加了這么多的屬性,并且還為這些屬性附了值,那么是希望程序讀取這些值,進(jìn)行使用的。那其實(shí)就是要看如何拿到這些注解配置的值。
測(cè)試:
MyAnnotition.java:
package annotation_;import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;import java.lang.annotation.Retention;import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;import java.lang.annotation.Target;@Target(ElementType.TYPE)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface MyAnnotation { String stringValue() default 'xxx'; int integerValue();}
TestCode.java:
package annotation_;@MyAnnotation(integerValue = 1)public class TestCode { public static void main(String[] args) { Class<TestCode> testCodeClass = TestCode.class; MyAnnotation myAnnotation = testCodeClass.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class); int i = myAnnotation.integerValue(); String s = myAnnotation.stringValue(); System.out.printf('i = %d, s = %sn', i, s); }}
輸出結(jié)果:
Connected to the target VM, address: ’127.0.0.1:49586’, transport: ’socket’i = 1, s = xxxDisconnected from the target VM, address: ’127.0.0.1:49586’, transport: ’socket’
Process finished with exit code 0
是不是感覺可以當(dāng)配置文件使用。但是最主要的問(wèn)題是myAnnotation.integerValue(),myAnnotation.stringValue()為什么可以拿到對(duì)應(yīng)的值,這個(gè)也是最核心的問(wèn)題。
那就是getAnnotation里面返回了一個(gè)實(shí)現(xiàn)了MyAnnotation注解(注解的本質(zhì)是接口)的實(shí)例。這個(gè)類大概是長(zhǎng)這樣的。
package annotation_;import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;public class MyAnnotationImpl implements MyAnnotation{ public String stringValue() { return 'xxx'; } public int integerValue() { return 0; } public Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType() { return null; }}
所以就可以通過(guò)抽象方法獲取到對(duì)應(yīng)的值。(如何生成這樣的一個(gè)類,只是學(xué)習(xí)注解,可以不關(guān)心。要不然,只能看里面的源碼。因?yàn)槿绻远x注解,你只會(huì)用到這一步,去獲取值。)
以上就是本文的全部?jī)?nèi)容,希望對(duì)大家的學(xué)習(xí)有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)。
相關(guān)文章:
1. Python實(shí)現(xiàn)迪杰斯特拉算法過(guò)程解析2. JavaScript Reduce使用詳解3. 淺談JavaScript中等號(hào)、雙等號(hào)、 三等號(hào)的區(qū)別4. Spring security 自定義過(guò)濾器實(shí)現(xiàn)Json參數(shù)傳遞并兼容表單參數(shù)(實(shí)例代碼)5. 詳解Python模塊化編程與裝飾器6. python使用ctypes庫(kù)調(diào)用DLL動(dòng)態(tài)鏈接庫(kù)7. Python如何進(jìn)行時(shí)間處理8. python裝飾器三種裝飾模式的簡(jiǎn)單分析9. JavaScript中的AOP編程的基本實(shí)現(xiàn)10. 詳解java中static關(guān)鍵詞的作用
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備