Java Annotation注解相關原理代碼總結
Java.lang 中自帶的注解
@Override:表示當前的方法定義將覆蓋基類的方法。如果你不小心拼寫錯誤,或者方法簽名被錯誤拼寫的時候,編譯器就會發出錯誤提示。 @Deprecated:如果使用該注解的元素被調用,編譯器就會發出警告信息。 @SuppressWarnings:關閉不當的編譯器警告信息。 @SafeVarargs:在 Java 7 中加入用于禁止對具有泛型varargs參數的方法或構造函數的調用方發出警告。 @FunctionalInterface:Java 8 中加入用于表示類型聲明為函數式接口如何定義注解
以下是一個為標記注解(marker annotation), 不包含任何元素
package cn.haidnor.annotation;import java.lang.annotation.*;@Target(ElementType.METHOD)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface Test { }
注解的定義也需要一些元注解(meta-annoation),比如 @Target 和 @Retention。
@Target 定義你的注解可以應用在哪里(例如是方法還是字段)。
@Retention 定義了注解在哪里可用,在源代碼中(SOURCE),class文件(CLASS)中或者是在運行時(RUNTIME)。
Demo 簡單實例
定義注解
以下的代碼中。Target 定義只能在方法上使用,Retention 定義保留域
package cn.haidnor.annotation;import java.lang.annotation.*;@Target(ElementType.METHOD)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface UseCase { int id(); String description() default 'no description';}
在類中使用注解
package cn.haidnor.clazz;package cn.haidnor.clazz;import cn.haidnor.annotation.UseCase;import java.util.List;public class PasswordUtils { @UseCase(id = 47, description ='Passwords must contain at least one numeric') public boolean validatePassword(String passwd) { return (passwd.matches('w*dw*')); } @UseCase(id = 48) public String encryptPassword(String passwd) { return new StringBuilder(passwd).reverse().toString(); } @UseCase(id = 49, description = 'New passwords can’t equal previously used ones') public boolean checkForNewPassword( List<String> prevPasswords, String passwd) { return !prevPasswords.contains(passwd); }}
對以上 demo 中的代碼進行測試
package cn.haidnor.test;import cn.haidnor.annotation.UseCase;import cn.haidnor.clazz.PasswordUtils;import java.util.*;import java.util.function.Consumer;import java.util.stream.*;import java.lang.reflect.*;public class UseCaseTracker { public static void main(String[] args) { List<Integer> useCases = IntStream.range(44, 51).boxed().collect(Collectors.toList()); trackUseCases(useCases, PasswordUtils.class); } public static void trackUseCases(List<Integer> useCasesList, Class<?> clazz) { // getDeclaredMethods() 獲取所有公開的方法 for(Method m : clazz.getDeclaredMethods()) { // getAnnotation() 獲取指定注解 UseCase uc = m.getAnnotation(UseCase.class); if(uc != null) {System.out.print('Found Use Case ');// 提取注解元素值System.out.println(uc.id());// 提取注解元素值System.out.println(’t’ + uc.description());useCasesList.remove( Integer.valueOf( uc.id() ) ); } } // 迭代集合 useCasesList.forEach(new Consumer<Integer>() { @Override public void accept(Integer integer) {System.out.println('Missing use case ' + integer); } }); // 以上代碼可以使用箭頭行數簡寫 // useCasesList.forEach(i -> System.out.println('Missing use case ' + i)); }}
控制臺輸出結果
Found Use Case 47 Passwords must contain at least one numericFound Use Case 48 no descriptionFound Use Case 49 New passwords can’t equal previously used onesMissing use case 44Missing use case 45Missing use case 46Missing use case 50
元注解
Java 語言中目前有 5 種標準注解(前面介紹過),以及 5 種元注解。元注解用于注解其他的注解
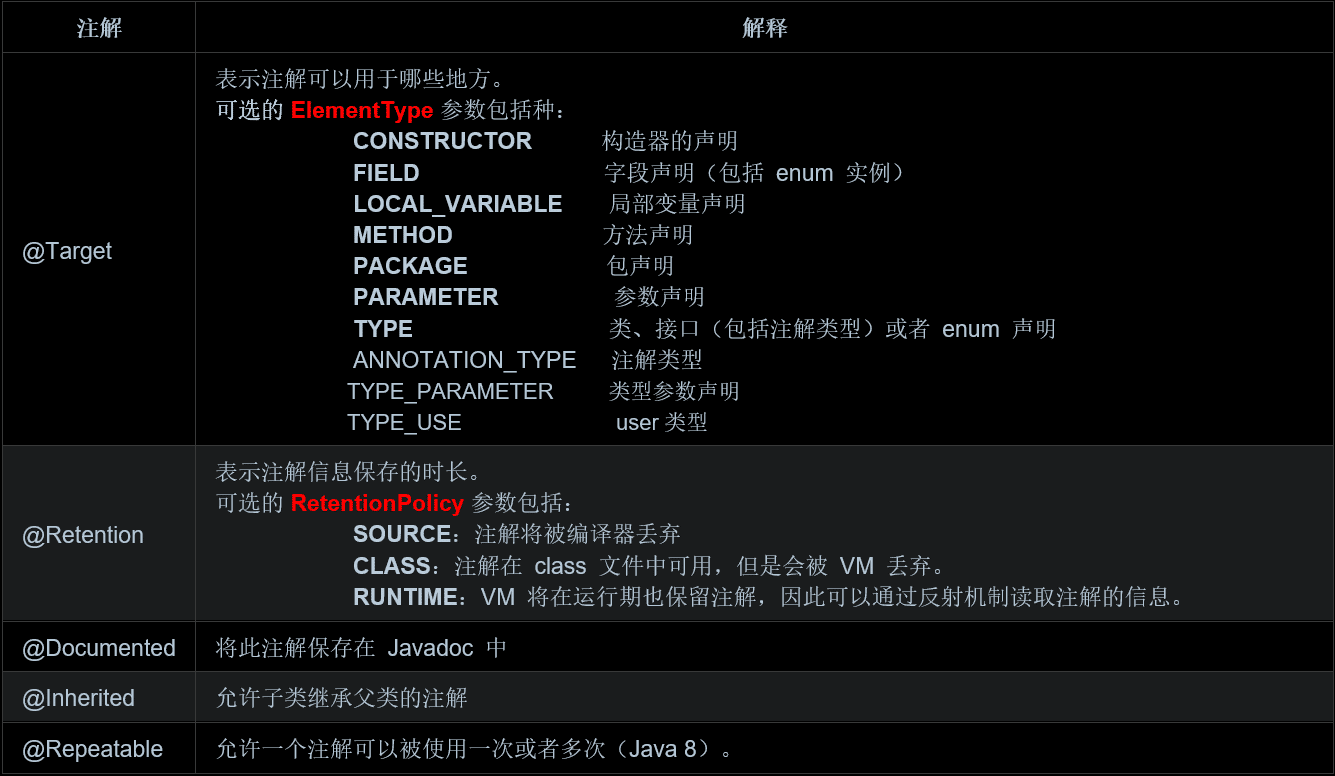
注解中可以使用的元素
所有基本類型(int、float、boolean等)
String Class enum Annotation 以上類型的數組其他類型,編譯器就會報錯。注意,也不允許使用任何包裝類型
注解的默認值無論是在源代碼聲明時還是在注解接口中定義默認值時,都不能使用 null 作為其值。
import java.lang.annotation.*;@Target(ElementType.METHOD)@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)public @interface SimulatingNull { int id() default -1; String description() default '';}
使用反射獲取注解的方法流程圖
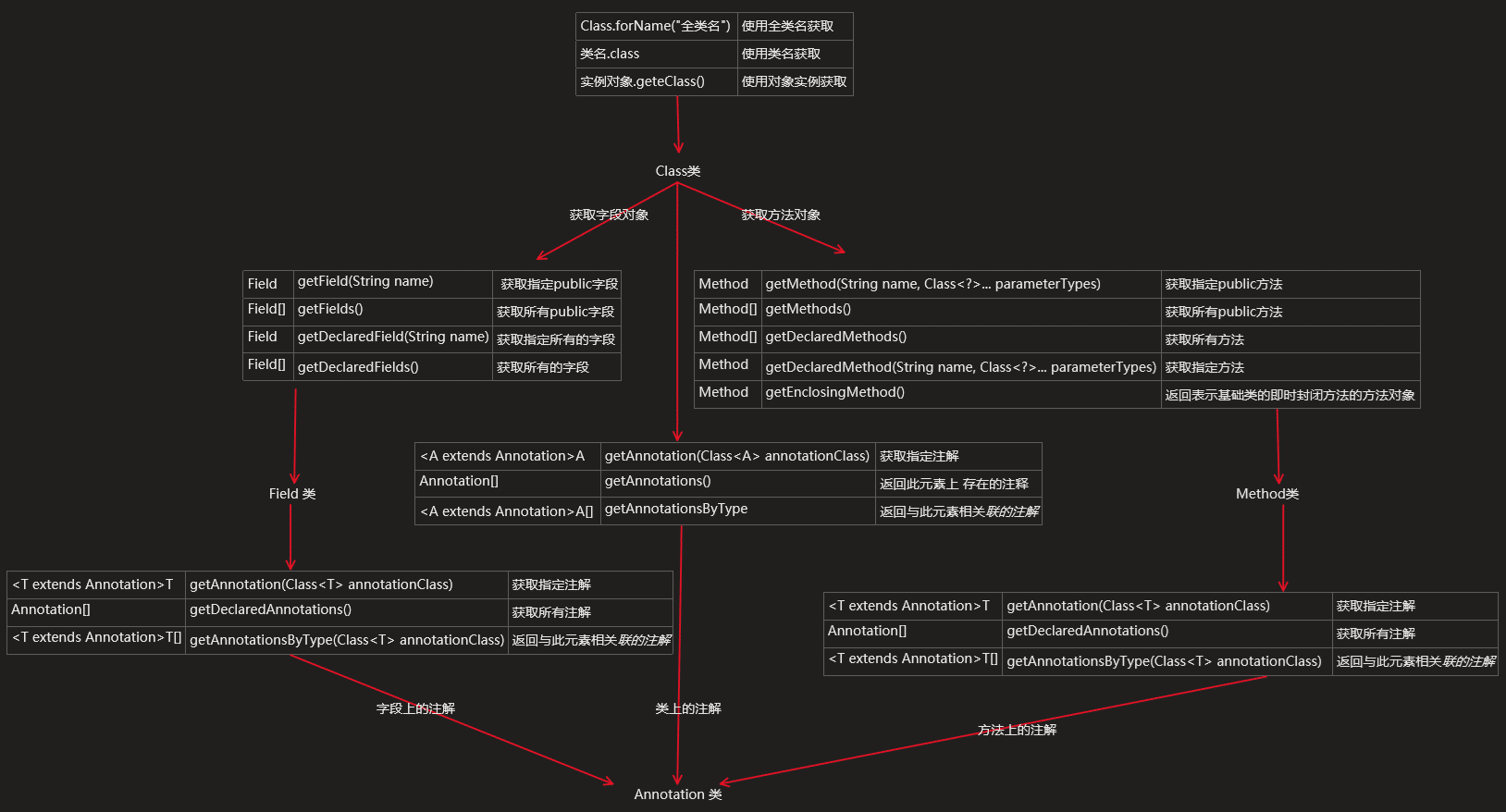
以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦網。
相關文章:

 網公網安備
網公網安備