Java容器源碼LinkedList原理解析
LinkedList簡介
LinkedList是一個使用雙向鏈表結(jié)構(gòu)實(shí)現(xiàn)的容器,與ArrayList一樣,它能動態(tài)擴(kuò)充其長度,LinkedList相較于ArrayList,其任意位置插入速度比ArrayList要快,但是其查詢速度要比ArrayList要慢;LinkedList繼承自AbstractSequentialList,實(shí)現(xiàn)了List、Deque、Cloneable、Serializable接口。
LinkedList UML圖如下:
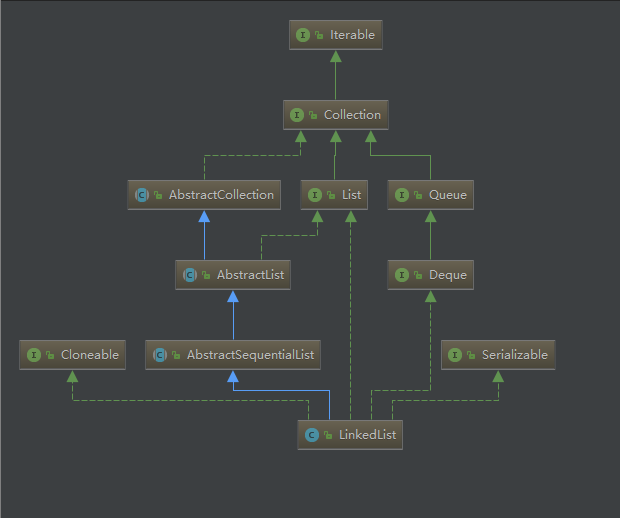
和ArrayList一樣,LinkedList也不是一個線程安全的容器。
LinkedList源碼分析
構(gòu)造方法
LinkedList有兩個構(gòu)造方法:
public LinkedList() {}//從已有的一個容器創(chuàng)建一個LinkedList對象public LinkedList(Collection<? extends E> c) { this(); addAll(c);}
addAll()方法:
public boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> c) { return addAll(size, c);}public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) { //檢查index是否溢出 checkPositionIndex(index); Object[] a = c.toArray(); int numNew = a.length; if (numNew == 0) return false; //獲取第index位置的node元素和node的前一個元素 //succ:第index位置的node元素 //pred:index位置前一個node元素 Node<E> pred, succ; if (index == size) { succ = null; pred = last; } else { succ = node(index); pred = succ.prev; } //遍歷,將元素插入鏈表中 for (Object o : a) { @SuppressWarnings('unchecked') E e = (E) o; Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, null); if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; pred = newNode; } if (succ == null) { last = pred; } else { pred.next = succ; succ.prev = pred; } size += numNew; modCount++; return true;}
add方法
LinkedList也有兩個add方法,如下:
public boolean add(E e) { //添加元素到隊(duì)尾 linkLast(e); return true;}public void add(int index, E element) { //檢查index是否溢出 checkPositionIndex(index); if (index == size) //index == size,直接添加到隊(duì)尾 linkLast(element); else //index != size,添加元素到index位置 linkBefore(element, node(index));}
linkLast方法:
void linkLast(E e) { final Node<E> l = last; //新建一個node,將其前一個元素指針指向原鏈表的最后一個元素 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(l, e, null); //更新尾指針 last = newNode; if (l == null) //若原last==null說明此時(shí)鏈表就一個元素 first = newNode; else //更新原鏈表尾元素指針 l.next = newNode; size++; modCount++;}
linkBefore方法:
void linkBefore(E e, Node<E> succ) { // assert succ != null; //獲取指定位node元素的前一個元素pred final Node<E> pred = succ.prev; //新建一個node,將其前指針指向pred元素 final Node<E> newNode = new Node<>(pred, e, succ); //將指定位置的node元素的前指針指向新元素,完成插入 succ.prev = newNode; if (pred == null) first = newNode; else pred.next = newNode; size++; modCount++;}
獲取指定位置node指針方法node:
Node<E> node(int index) { // assert isElementIndex(index); //index > size/2時(shí),說明在鏈表前半段,從前往后搜索 if (index < (size >> 1)) { Node<E> x = first; for (int i = 0; i < index; i++) x = x.next; return x; //index < size/2時(shí),從后往前搜索 } else { Node<E> x = last; for (int i = size - 1; i > index; i--) x = x.prev; return x; }}
get方法也比較簡單,首先檢測index是否溢出,然后直接找到index位置的元素,并返回其item。
以上就是本文的全部內(nèi)容,希望對大家的學(xué)習(xí)有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦網(wǎng)。
相關(guān)文章:
1. Django視圖類型總結(jié)2. Xml簡介_動力節(jié)點(diǎn)Java學(xué)院整理3. 使用Docker的NFS-Ganesha鏡像搭建nfs服務(wù)器的詳細(xì)過程4. Intellij IDEA 關(guān)閉和開啟自動更新的提示?5. Ajax引擎 ajax請求步驟詳細(xì)代碼6. 解析原生JS getComputedStyle7. idea重置默認(rèn)配置的方法步驟8. IntelliJ IDEA Java項(xiàng)目手動添加依賴 jar 包的方法(圖解)9. Django使用HTTP協(xié)議向服務(wù)器傳參方式小結(jié)10. Spring @Profile注解實(shí)現(xiàn)多環(huán)境配置
 網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備
網(wǎng)公網(wǎng)安備