Python3 filecmp模塊測試比較文件原理解析
1.filecmp比較文件
filecmp模塊提供了一些函數和一個類來比較文件系統上的文件和目錄。
1.1 示例數據
使用下面代碼創建一組測試文件。
import osdef mkfile(filename, body=None): with open(filename, ’w’) as f: f.write(body or filename) return def make_example_dir(top): if not os.path.exists(top): os.mkdir(top) curdir = os.getcwd() os.chdir(top) os.mkdir(’dir1’) os.mkdir(’dir2’) mkfile(’dir1/file_only_in_dir1’) mkfile(’dir2/file_only_in_dir2’) os.mkdir(’dir1/dir_only_in_dir1’) os.mkdir(’dir2/dir_only_in_dir2’) os.mkdir(’dir1/common_dir’) os.mkdir(’dir2/common_dir’) mkfile(’dir1/common_file’, ’this file is the same’) os.link(’dir1/common_file’, ’dir2/common_file’) mkfile(’dir1/contents_differ’) mkfile(’dir2/contents_differ’) # Update the access and modification times so most of the stat # results will match. st = os.stat(’dir1/contents_differ’) os.utime(’dir2/contents_differ’, (st.st_atime, st.st_mtime)) mkfile(’dir1/file_in_dir1’, ’This is a file in dir1’) os.mkdir(’dir2/file_in_dir1’) os.chdir(curdir) return if __name__ == ’__main__’: os.chdir(os.path.dirname(__file__) or os.getcwd()) make_example_dir(’example’) make_example_dir(’example/dir1/common_dir’) make_example_dir(’example/dir2/common_dir’)
運行這個腳本會在axample目錄下生成一個文件樹。
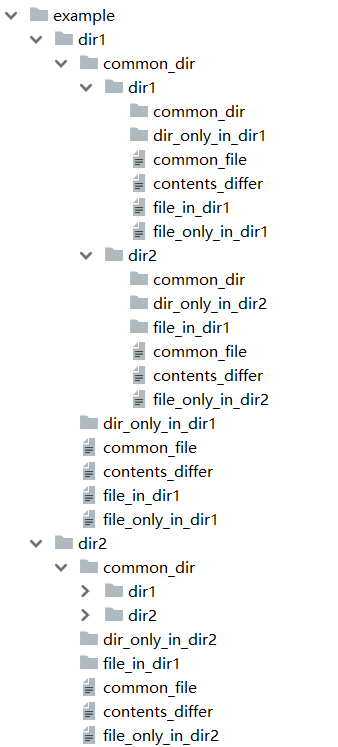
common_dir目錄下也有同樣的目錄結構,以提供有意思的遞歸比較選擇。
1.2 比較文件
cmp()用于比較文件系統上的兩個文件。
import filecmpprint(’common_file :’, end=’ ’)print(filecmp.cmp(’example/dir1/common_file’, ’example/dir2/common_file’, shallow=True), end=’ ’)print(filecmp.cmp(’example/dir1/common_file’, ’example/dir2/common_file’, shallow=False))print(’contents_differ:’, end=’ ’)print(filecmp.cmp(’example/dir1/contents_differ’, ’example/dir2/contents_differ’, shallow=True), end=’ ’)print(filecmp.cmp(’example/dir1/contents_differ’, ’example/dir2/contents_differ’, shallow=False))print(’identical :’, end=’ ’)print(filecmp.cmp(’example/dir1/file_only_in_dir1’, ’example/dir1/file_only_in_dir1’, shallow=True), end=’ ’)print(filecmp.cmp(’example/dir1/file_only_in_dir1’, ’example/dir1/file_only_in_dir1’, shallow=False))
shallo參數告訴cmp()除了文件的元數據外,是否還要查看文件的內容。默認情況下,會使用由os.stat()得到的信息來完成一個淺比較。如果結果是一樣的,則認為文件相同。因此,對于同時創建的相同大小的文件,即使他們的內容不同,也會報告為是相同的文件。當shallow為False時,則要比較文件的內容。

如果非遞歸的比較兩個目錄中的一組文件,則可以使用cmpfiles()。參數是目錄名和兩個位置上要檢查的我就愛你列表。傳入的公共文件列表應當只包含文件名(目錄會導致匹配不成功),而且這些文件在兩個位置上都應當出現。下一個例子顯示了構造公共列表的一種簡單方法。與cmp()一樣,這個比較也有一個shallow標志。
import filecmpimport os# Determine the items that exist in both directoriesd1_contents = set(os.listdir(’example/dir1’))d2_contents = set(os.listdir(’example/dir2’))common = list(d1_contents & d2_contents)common_files = [ f for f in common if os.path.isfile(os.path.join(’example/dir1’, f))]print(’Common files:’, common_files)# Compare the directoriesmatch, mismatch, errors = filecmp.cmpfiles( ’example/dir1’, ’example/dir2’, common_files,)print(’Match :’, match)print(’Mismatch :’, mismatch)print(’Errors :’, errors)
cmpfiles()返回3個文件名列表,分別包含匹配的文件、不匹配的文件和不能比較的文件(由于權限問題或出于其他原因)。

1.3 比較目錄
前面介紹的函數適合完成相對簡單的比較。對于大目錄樹的遞歸比較或者更完整的分析,dircmp類很更有用。在最簡單的用例中,report()會打印比較兩個目錄的報告。
import filecmpdc = filecmp.dircmp(’example/dir1’, ’example/dir2’)dc.report()
輸出是一個純文本報告,顯示的結果只包括給定目錄的內容,而不會遞歸比較其子目錄。在這里,認為文件not_the_same是相同的,因為這里沒有比較內容。無法讓dircmp像cmp()那樣比較文件的內容。

為了更多的細節,也為了完成一個遞歸比較,可以使用report_full_closure()。
import filecmpdc = filecmp.dircmp(’example/dir1’, ’example/dir2’)dc.report_full_closure()
輸出將包括所有同級子目錄的比較。

1.4 在程序中使用差異
除了生成打印報告,dircmp還能計算文件列表,可以在程序中直接使用。以下各個屬性只在請求時才計算,所以對于未用的數據,創建dircmp實例不會帶來開銷。
import filecmpimport pprintdc = filecmp.dircmp(’example/dir1’, ’example/dir2’)print(’Left:’)pprint.pprint(dc.left_list)print(’nRight:’)pprint.pprint(dc.right_list)
所比較目錄中包含的文件和子目錄分別列在left_list和right_list中。

可以向構造函數傳入一個要忽略的名字列表(該列表中指定的名字將被忽略)來對輸入進行過濾。默認的,RCS、CVS和tags等名字會被忽略。
import filecmpimport pprintdc = filecmp.dircmp(’example/dir1’, ’example/dir2’, ignore=[’common_file’])print(’Left:’)pprint.pprint(dc.left_list)print(’nRight:’)pprint.pprint(dc.right_list)
在這里,將common_file從要比較的文件列表中去除。

兩個輸入目錄中共有的文件名會保存在common內,各目錄獨有的文件會列在left_only和right_only中。
import filecmpimport pprintdc = filecmp.dircmp(’example/dir1’, ’example/dir2’)print(’Common:’)pprint.pprint(dc.common)print(’nLeft:’)pprint.pprint(dc.left_only)print(’nRight:’)pprint.pprint(dc.right_only)
'左'目錄是dircmp()的第一個參數,'右'目錄是第二個參數。

公共成員可以被進一步分解為文件、目錄和“有趣”元素(兩個目錄中類型不同的內容,或者os.stat()指出的有錯誤的地方)。
import filecmpimport pprintdc = filecmp.dircmp(’example/dir1’, ’example/dir2’)print(’Common:’)pprint.pprint(dc.common)print(’nDirectories:’)pprint.pprint(dc.common_dirs)print(’nFiles:’)pprint.pprint(dc.common_files)print(’nFunny:’)pprint.pprint(dc.common_funny)
在示例數據中,file_in_dir1元素在一個目錄中是一個文件,而在另一個目錄中是一個子目錄,所以它會出現在“有趣”列表中。

文件之間的差別也可以做類似的劃分。
import filecmpdc = filecmp.dircmp(’example/dir1’, ’example/dir2’)print(’Same :’, dc.same_files)print(’Different :’, dc.diff_files)print(’Funny :’, dc.funny_files)
文件not_the_same通過os.stat()比較,并且不檢查內容,所以它包含在same_files列表中。

最后一點,子目錄也會被保存,以便容易地完成遞歸比較。
import filecmpdc = filecmp.dircmp(’example/dir1’, ’example/dir2’)print(’Subdirectories:’)print(dc.subdirs)
屬性subdirs是一個字典,它將目錄名映射到新的dircmp對象。

以上就是本文的全部內容,希望對大家的學習有所幫助,也希望大家多多支持好吧啦網。
相關文章:
 網公網安備
網公網安備